
2.1 Context: European Colonization
5 min read•april 16, 2023
James Glackin
Jed Quiaoit
James Glackin
Jed Quiaoit
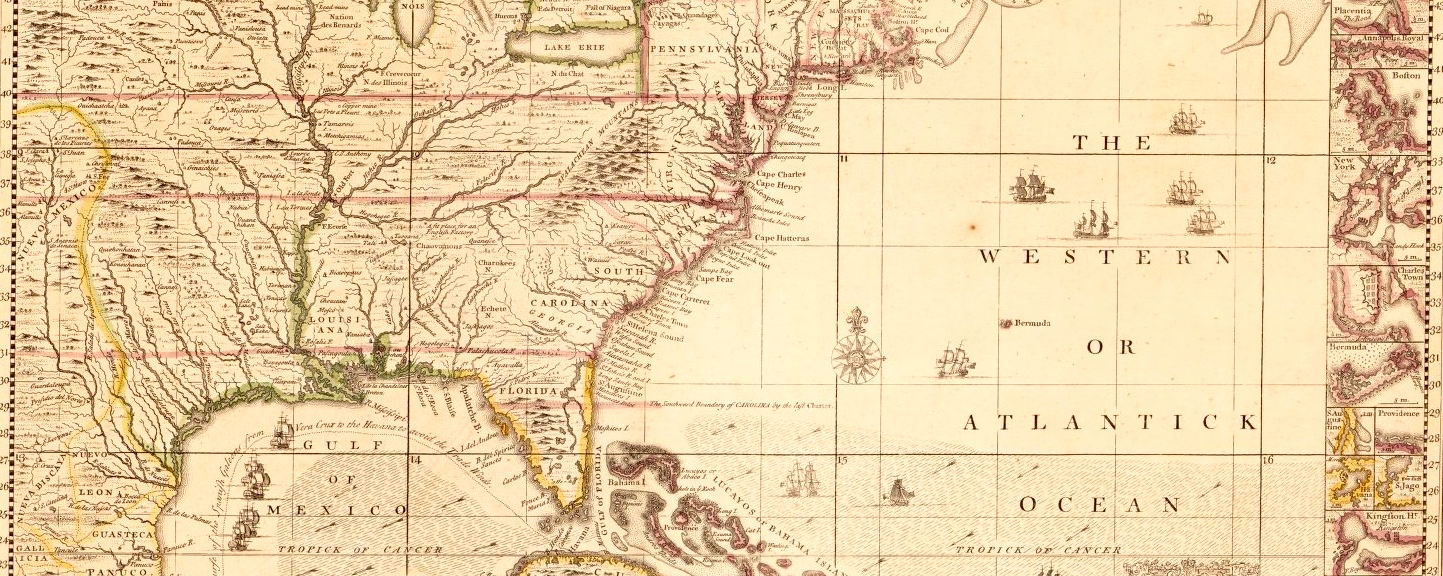
Henry Popple, A map of the British Empire in America with the French and Spanish settlements adjacent thereto, 1733. Library of Congress.
The colonization of North America from 1607 to 1754 was a complex and multifaceted process that was shaped by a variety of factors. European nations, including , , the , and , each had their own motivations for colonizing the continent, which included economic, imperial, and religious goals. These goals, along with the different cultures and environments of the colonizing nations, led to the development of distinct colonization and migration patterns.
For example, the Spanish focused on the extraction of precious metals and other resources from , while the French focused on fur trading and the development of settlements along the Mississippi and St. Lawrence Rivers. The Dutch established trading posts in the northeastern regions of the continent, while the British established colonies along the , with a focus on the development of and other cash crops. 🚬
Additionally, competition for resources between European rivals and American Indians led to increased industry and trade, as well as conflicts over land and resources. This competition also had a major impact on the development of the colonies, as European nations sought to gain control of key resources and strategic locations. This competition and conflict would eventually lead to the from 1754 to 1763, also known as the , which would significantly impact the balance of power in North America and pave the way for British dominance on the continent.
Case Studies
The different economic and imperial goals of these colonizers had a significant impact on the social and political development of their colonies, as well as their relationships with native populations. For example, the , which forced indigenous peoples to work for Spanish colonizers, led to significant exploitation and conflict, while the French tended to have a more cooperative relationship with native tribes. 🤔
British Colonization
The British colonies in North America participated in a complex and dynamic relationship with throughout the colonial period. While the colonies were heavily influenced by British political, social, and cultural norms, they also developed their own distinct identities and cultural practices. This led to tension between the colonies' desire for stronger bonds with and their resistance to British control.
Such variety was evident in the various political and economic exchanges between the colonies and , as well as in the cultural and social interactions that took place between colonizers and colonized.
also played a significant role in shaping the political and cultural attitudes of the colonists. The commercial, religious, philosophical, and political exchanges that took place between the colonies and , as well as between the colonies themselves, led to a growing sense of interconnectedness among the colonists. This led to the development of a unique American identity over time, as well as a growing sense of dissatisfaction with British rule. 😡
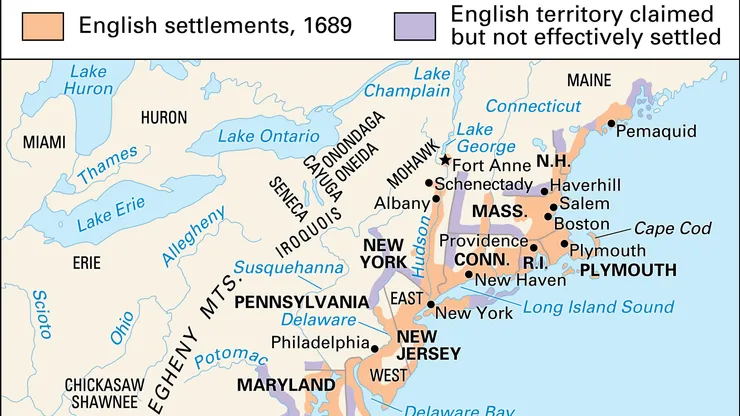
Source: Encyclopedia Britannica
was also a pivotal part of the colonial system in British North America, as it was in other European empires in the Americas. The English colonies developed a vicious system of that reflected the specific economic, demographic, and geographic characteristics of those colonies. The use of enslaved Africans was crucial to the development of cash crops like and , which were the main economic drivers of the colonies.
The slave trade also had a significant impact on the demographic makeup of the colonies, as the aforementioned enslaved Africans made up a significant portion of the population. The use of enslaved labor was more prevalent in the , where the climate and soil were more conducive to the cultivation of cash crops. Ultimately, the slave trade became a major source of profit for British merchants and influenced the economic development of the entire . 🇬🇧
Spanish Colonization
In the 15th century, the Spanish set their sights on the Americas, driven by the desire for gold, God, and glory. They laid claim to lands in the southwestern and western parts of North America, including the conquest of . Their expansion continued in , where they established the encomienda system of forced labor, which primarily targeted native peoples. 🏆
Due to the lack of women among the Spanish colonizers, they intermarried with the local indigenous populations, resulting in a mixed-race population known as . However, the Spanish treatment of the native populations was often brutal, as seen in their interactions with the of the Southwest. In 1609, they established the colony of in and set up , imposing on the .
The would eventually resist this forced conversion and colonization in the form of in 1680. They killed Spanish priests and hundreds of settlers, successfully driving the Spanish out for the next 50 years. However, the Spanish would eventually reclaim the colony, reasserting their control over the and the region.
French Colonization
Under the rule of , solidified its position as a major world power. In an effort to expand its empire, established a permanent settlement in in 1608, as well as other parts of northeastern North America, which would become known as or . The French explorer played a key role in the colonization of , creating an alliance with the local Huron Indians and helping them defeat their enemies.
The French also aimed to control the strategically important , which would link their northern holdings in with their southern holdings in the . However, this goal would bring them into conflict with the , who had allied themselves with the British.
The French and British would engage in numerous battles for control of the , as the French sought to maintain their grip on the region and the British sought to expand their own empire. These battles would have a significant impact on the outcome of the larger struggle between and for control of North America. ⚔️
As we move forward, we'll continue developing and adding to the context of the colonial period in North America by highlighting the interactions and conflicts between European colonizers and the native populations, as well as the impact of on the political and cultural attitudes of the colonists.
Additionally, we'll also delve into the system of that developed in the colonies and how it was shaped by the specific economic, demographic, and geographic characteristics of the region.
Key Terms to Review (42)
A map of the British Empire in America with French and Spanish settlements adjacent thereto
: This is one of Henry Popple's most famous works. It's a detailed map showing not only British territories in North America but also nearby French and Spanish settlements.Atlantic Coast
: The Atlantic Coast refers to the easternmost coastlines along the Atlantic Ocean in North America which includes all coastal states from Maine down to Florida.Britain
: Britain, also known as the United Kingdom, is a country located off the northwestern coast of mainland Europe. In the context of AP US History, it's particularly important because it was the colonial power that established 13 colonies on the east coast of North America, which later became the United States.British Empire
: The British Empire was a group of territories, colonies, and countries controlled by Britain from the late 16th to early 20th century. It was one of the largest empires in history and had significant influence over global politics, economics, and culture.Canada
: A country in North America, located to the north of the United States. It was first explored by Europeans in the late 15th century and later colonized by both the French and British.Catholic missions
: These were religious communities established by the Catholic Church during the 16th to 19th centuries. Their purpose was to spread Christianity among local indigenous populations in newly discovered areas of the world.Central and South America
: These are regions in Americas located south of Mexico. They were home to advanced civilizations such as Maya & Aztec before being colonized primarily by Spain & Portugal during Age of Discovery.Christianity
: Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ as presented in the New Testament. It's one of the largest religions in the world, with followers known as Christians.Encomienda System
: The encomienda system was a labor system instituted by Spain in American colonies where settlers were granted land and given control over local indigenous people who were compelled to work for them in exchange for conversion to Christianity and protection.Encyclopedia Britannica
: The Encyclopedia Britannica is a general knowledge English-language encyclopedia which was first published in Scotland in 1768. It has been revised regularly since then with new editions reflecting advancements in various fields.Florida
: Florida is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States, known for its warm climate and extensive coastline.France
: France, like Spain, was another significant European power involved in colonizing parts of North America from 16th century onwards, particularly areas now known as Canada and Louisiana.French and Indian War
: The French and Indian War was a conflict in North America, lasting from 1754 to 1763, that represented colonial events related to the European conflict known as the Seven Years' War.Great Britain
: Great Britain is an island that includes England, Scotland, and Wales. It's also often used to refer to the United Kingdom, which includes Northern Ireland. During its height in 19th century, it was considered a global superpower with vast overseas empire.Henry Popple
: Henry Popple was a British cartographer in the 18th century, best known for his detailed map of the British Empire in America.Huron Indians
: A group of Native American people historically located in the region of the eastern Great Lakes. They were heavily involved in fur trade with European settlers.Iroquois
: The Iroquois were a powerful Native American confederacy in North America, consisting of six tribes: the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, Seneca, and Tuscarora. They played a significant role in colonial-era politics and warfare.King Louis XIV
: King Louis XIV, also known as the Sun King, was a monarch of the House of Bourbon who reigned as King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign is often associated with the concept of absolute monarchy and he played a key role in the development of French colonialism.Latin America
: Latin America refers to the region of the Americas where Romance languages (Spanish, Portuguese, and French) are primarily spoken. It includes countries in Central and South America, Mexico, and parts of the Caribbean.Library of Congress
: The Library of Congress is the largest library in the world, with millions of books, recordings, photographs, maps and manuscripts in its collections. It serves as the main research arm of the U.S. Congress and is home to the U.S. Copyright Office.Lower Mississippi Valley
: The Lower Mississippi Valley refers to the region along the lower part of the Mississippi River, from Memphis, Tennessee down to the Gulf of Mexico. It was a key area for agriculture and trade in early American history.Mestizos
: Mestizos are individuals of mixed racial ancestry, specifically of European (Spanish or Portuguese) and indigenous American descent.Mississippi River
: The Mississippi River is a major waterway in North America that flows south from northern Minnesota to the Gulf of Mexico. It played a crucial role in the development and expansion of American society, particularly during westward expansion.Netherlands
: The Netherlands, also known as Dutch, were involved in early exploration and colonization of North America during the 17th century, most notably establishing New Netherland which included parts of present-day New York.New France
: New France was a territory in North America that was claimed by France from 1534 until it was ceded to Great Britain and Spain in 1763. It included parts of what is now Quebec, Canada, as well as other territories in North America.New Mexico
: New Mexico is a state located in the Southwestern region of the United States. It's known for its diverse culture with influences from Native American, Hispanic, and Anglo-American traditions.Ohio River Valley
: The Ohio River Valley is a crucial geographical area in U.S. history that served as a contested borderland between French and British territories before becoming an important part of westward expansion after independence.Popé's Rebellion
: Also known as the Pueblo Revolt, this was an uprising in 1680 by indigenous Pueblo people against Spanish colonizers in what is now New Mexico. The rebellion, led by a man named Popé, successfully expelled the Spanish for over a decade.Pueblo People
: The Pueblo people are Native American tribes who live in the Southwestern United States, particularly in Arizona and New Mexico. They are known for their unique architecture of multi-story houses made from adobe or stone.Quebec
: Quebec is a province located in eastern Canada. It was one of the first parts of North America to be explored and settled by Europeans. In AP US History context, it's significant because it was established by France as part its New France colony.Rice
: Rice is a staple crop that has been cultivated worldwide. In AP US History context, rice plantations were particularly important in Southern colonies where conditions were ideal for its growth.Samuel de Champlain
: A French explorer who founded Quebec City in 1608 and is often referred to as "The Father of New France". He also mapped much of northeastern North America and started relationships with several Native American tribes.Santa Fe
: Santa Fe is the capital of New Mexico and one of the oldest cities in the United States. It's known for its Pueblo-style architecture and vibrant arts scene.Seven Years' War
: The Seven Years' War was a global conflict fought between 1756 and 1763. It involved every European great power of the time and spanned five continents, affecting Europe, the Americas, West Africa, India, and the Philippines.Slavery
: Slavery is a system in which individuals, known as slaves, are treated as property and forced to work without consent or pay. In the context of US history, it refers primarily to the African slave trade from the 16th to 19th centuries.Southern Colonies
: These were five British colonies located south along Atlantic coast - Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia. They were known for their agricultural economy, particularly tobacco and rice cultivation.Southwestern North America
: Southwestern North America is a region that includes parts of Mexico and United States (Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, Utah). It's known for its desert landscapes but also has mountains and forests.Spain
: A country located on the Iberian Peninsula in Europe. In AP US History context it is known for being one of major colonial powers in Americas during Age Of Discovery .Spanish encomienda system
: The encomienda system was established by Spain during their colonization period in Americas during 16th century. It allowed colonists to demand labor or tribute from indigenous people in exchange for providing protection and Christian education.St. Lawrence River
: The St. Lawrence River is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America, connecting the Great Lakes with the Atlantic Ocean.Tobacco
: A cash crop that was grown primarily in the Southern colonies of North America during the 17th and 18th centuries. It played a significant role in the economy of these colonies.Transatlantic exchanges
: The transatlantic exchanges refer to the transfer of people, goods, diseases, and ideas between the New World (Americas) and the Old World (Europe, Africa, Asia) following Christopher Columbus's voyage in 1492. This is also known as the Columbian Exchange.2.1 Context: European Colonization
5 min read•april 16, 2023
James Glackin
Jed Quiaoit
James Glackin
Jed Quiaoit

Henry Popple, A map of the British Empire in America with the French and Spanish settlements adjacent thereto, 1733. Library of Congress.
The colonization of North America from 1607 to 1754 was a complex and multifaceted process that was shaped by a variety of factors. European nations, including , , the , and , each had their own motivations for colonizing the continent, which included economic, imperial, and religious goals. These goals, along with the different cultures and environments of the colonizing nations, led to the development of distinct colonization and migration patterns.
For example, the Spanish focused on the extraction of precious metals and other resources from , while the French focused on fur trading and the development of settlements along the Mississippi and St. Lawrence Rivers. The Dutch established trading posts in the northeastern regions of the continent, while the British established colonies along the , with a focus on the development of and other cash crops. 🚬
Additionally, competition for resources between European rivals and American Indians led to increased industry and trade, as well as conflicts over land and resources. This competition also had a major impact on the development of the colonies, as European nations sought to gain control of key resources and strategic locations. This competition and conflict would eventually lead to the from 1754 to 1763, also known as the , which would significantly impact the balance of power in North America and pave the way for British dominance on the continent.
Case Studies
The different economic and imperial goals of these colonizers had a significant impact on the social and political development of their colonies, as well as their relationships with native populations. For example, the , which forced indigenous peoples to work for Spanish colonizers, led to significant exploitation and conflict, while the French tended to have a more cooperative relationship with native tribes. 🤔
British Colonization
The British colonies in North America participated in a complex and dynamic relationship with throughout the colonial period. While the colonies were heavily influenced by British political, social, and cultural norms, they also developed their own distinct identities and cultural practices. This led to tension between the colonies' desire for stronger bonds with and their resistance to British control.
Such variety was evident in the various political and economic exchanges between the colonies and , as well as in the cultural and social interactions that took place between colonizers and colonized.
also played a significant role in shaping the political and cultural attitudes of the colonists. The commercial, religious, philosophical, and political exchanges that took place between the colonies and , as well as between the colonies themselves, led to a growing sense of interconnectedness among the colonists. This led to the development of a unique American identity over time, as well as a growing sense of dissatisfaction with British rule. 😡

Source: Encyclopedia Britannica
was also a pivotal part of the colonial system in British North America, as it was in other European empires in the Americas. The English colonies developed a vicious system of that reflected the specific economic, demographic, and geographic characteristics of those colonies. The use of enslaved Africans was crucial to the development of cash crops like and , which were the main economic drivers of the colonies.
The slave trade also had a significant impact on the demographic makeup of the colonies, as the aforementioned enslaved Africans made up a significant portion of the population. The use of enslaved labor was more prevalent in the , where the climate and soil were more conducive to the cultivation of cash crops. Ultimately, the slave trade became a major source of profit for British merchants and influenced the economic development of the entire . 🇬🇧
Spanish Colonization
In the 15th century, the Spanish set their sights on the Americas, driven by the desire for gold, God, and glory. They laid claim to lands in the southwestern and western parts of North America, including the conquest of . Their expansion continued in , where they established the encomienda system of forced labor, which primarily targeted native peoples. 🏆
Due to the lack of women among the Spanish colonizers, they intermarried with the local indigenous populations, resulting in a mixed-race population known as . However, the Spanish treatment of the native populations was often brutal, as seen in their interactions with the of the Southwest. In 1609, they established the colony of in and set up , imposing on the .
The would eventually resist this forced conversion and colonization in the form of in 1680. They killed Spanish priests and hundreds of settlers, successfully driving the Spanish out for the next 50 years. However, the Spanish would eventually reclaim the colony, reasserting their control over the and the region.
French Colonization
Under the rule of , solidified its position as a major world power. In an effort to expand its empire, established a permanent settlement in in 1608, as well as other parts of northeastern North America, which would become known as or . The French explorer played a key role in the colonization of , creating an alliance with the local Huron Indians and helping them defeat their enemies.
The French also aimed to control the strategically important , which would link their northern holdings in with their southern holdings in the . However, this goal would bring them into conflict with the , who had allied themselves with the British.
The French and British would engage in numerous battles for control of the , as the French sought to maintain their grip on the region and the British sought to expand their own empire. These battles would have a significant impact on the outcome of the larger struggle between and for control of North America. ⚔️
As we move forward, we'll continue developing and adding to the context of the colonial period in North America by highlighting the interactions and conflicts between European colonizers and the native populations, as well as the impact of on the political and cultural attitudes of the colonists.
Additionally, we'll also delve into the system of that developed in the colonies and how it was shaped by the specific economic, demographic, and geographic characteristics of the region.
Key Terms to Review (42)
A map of the British Empire in America with French and Spanish settlements adjacent thereto
: This is one of Henry Popple's most famous works. It's a detailed map showing not only British territories in North America but also nearby French and Spanish settlements.Atlantic Coast
: The Atlantic Coast refers to the easternmost coastlines along the Atlantic Ocean in North America which includes all coastal states from Maine down to Florida.Britain
: Britain, also known as the United Kingdom, is a country located off the northwestern coast of mainland Europe. In the context of AP US History, it's particularly important because it was the colonial power that established 13 colonies on the east coast of North America, which later became the United States.British Empire
: The British Empire was a group of territories, colonies, and countries controlled by Britain from the late 16th to early 20th century. It was one of the largest empires in history and had significant influence over global politics, economics, and culture.Canada
: A country in North America, located to the north of the United States. It was first explored by Europeans in the late 15th century and later colonized by both the French and British.Catholic missions
: These were religious communities established by the Catholic Church during the 16th to 19th centuries. Their purpose was to spread Christianity among local indigenous populations in newly discovered areas of the world.Central and South America
: These are regions in Americas located south of Mexico. They were home to advanced civilizations such as Maya & Aztec before being colonized primarily by Spain & Portugal during Age of Discovery.Christianity
: Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ as presented in the New Testament. It's one of the largest religions in the world, with followers known as Christians.Encomienda System
: The encomienda system was a labor system instituted by Spain in American colonies where settlers were granted land and given control over local indigenous people who were compelled to work for them in exchange for conversion to Christianity and protection.Encyclopedia Britannica
: The Encyclopedia Britannica is a general knowledge English-language encyclopedia which was first published in Scotland in 1768. It has been revised regularly since then with new editions reflecting advancements in various fields.Florida
: Florida is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States, known for its warm climate and extensive coastline.France
: France, like Spain, was another significant European power involved in colonizing parts of North America from 16th century onwards, particularly areas now known as Canada and Louisiana.French and Indian War
: The French and Indian War was a conflict in North America, lasting from 1754 to 1763, that represented colonial events related to the European conflict known as the Seven Years' War.Great Britain
: Great Britain is an island that includes England, Scotland, and Wales. It's also often used to refer to the United Kingdom, which includes Northern Ireland. During its height in 19th century, it was considered a global superpower with vast overseas empire.Henry Popple
: Henry Popple was a British cartographer in the 18th century, best known for his detailed map of the British Empire in America.Huron Indians
: A group of Native American people historically located in the region of the eastern Great Lakes. They were heavily involved in fur trade with European settlers.Iroquois
: The Iroquois were a powerful Native American confederacy in North America, consisting of six tribes: the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, Seneca, and Tuscarora. They played a significant role in colonial-era politics and warfare.King Louis XIV
: King Louis XIV, also known as the Sun King, was a monarch of the House of Bourbon who reigned as King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign is often associated with the concept of absolute monarchy and he played a key role in the development of French colonialism.Latin America
: Latin America refers to the region of the Americas where Romance languages (Spanish, Portuguese, and French) are primarily spoken. It includes countries in Central and South America, Mexico, and parts of the Caribbean.Library of Congress
: The Library of Congress is the largest library in the world, with millions of books, recordings, photographs, maps and manuscripts in its collections. It serves as the main research arm of the U.S. Congress and is home to the U.S. Copyright Office.Lower Mississippi Valley
: The Lower Mississippi Valley refers to the region along the lower part of the Mississippi River, from Memphis, Tennessee down to the Gulf of Mexico. It was a key area for agriculture and trade in early American history.Mestizos
: Mestizos are individuals of mixed racial ancestry, specifically of European (Spanish or Portuguese) and indigenous American descent.Mississippi River
: The Mississippi River is a major waterway in North America that flows south from northern Minnesota to the Gulf of Mexico. It played a crucial role in the development and expansion of American society, particularly during westward expansion.Netherlands
: The Netherlands, also known as Dutch, were involved in early exploration and colonization of North America during the 17th century, most notably establishing New Netherland which included parts of present-day New York.New France
: New France was a territory in North America that was claimed by France from 1534 until it was ceded to Great Britain and Spain in 1763. It included parts of what is now Quebec, Canada, as well as other territories in North America.New Mexico
: New Mexico is a state located in the Southwestern region of the United States. It's known for its diverse culture with influences from Native American, Hispanic, and Anglo-American traditions.Ohio River Valley
: The Ohio River Valley is a crucial geographical area in U.S. history that served as a contested borderland between French and British territories before becoming an important part of westward expansion after independence.Popé's Rebellion
: Also known as the Pueblo Revolt, this was an uprising in 1680 by indigenous Pueblo people against Spanish colonizers in what is now New Mexico. The rebellion, led by a man named Popé, successfully expelled the Spanish for over a decade.Pueblo People
: The Pueblo people are Native American tribes who live in the Southwestern United States, particularly in Arizona and New Mexico. They are known for their unique architecture of multi-story houses made from adobe or stone.Quebec
: Quebec is a province located in eastern Canada. It was one of the first parts of North America to be explored and settled by Europeans. In AP US History context, it's significant because it was established by France as part its New France colony.Rice
: Rice is a staple crop that has been cultivated worldwide. In AP US History context, rice plantations were particularly important in Southern colonies where conditions were ideal for its growth.Samuel de Champlain
: A French explorer who founded Quebec City in 1608 and is often referred to as "The Father of New France". He also mapped much of northeastern North America and started relationships with several Native American tribes.Santa Fe
: Santa Fe is the capital of New Mexico and one of the oldest cities in the United States. It's known for its Pueblo-style architecture and vibrant arts scene.Seven Years' War
: The Seven Years' War was a global conflict fought between 1756 and 1763. It involved every European great power of the time and spanned five continents, affecting Europe, the Americas, West Africa, India, and the Philippines.Slavery
: Slavery is a system in which individuals, known as slaves, are treated as property and forced to work without consent or pay. In the context of US history, it refers primarily to the African slave trade from the 16th to 19th centuries.Southern Colonies
: These were five British colonies located south along Atlantic coast - Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia. They were known for their agricultural economy, particularly tobacco and rice cultivation.Southwestern North America
: Southwestern North America is a region that includes parts of Mexico and United States (Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, Utah). It's known for its desert landscapes but also has mountains and forests.Spain
: A country located on the Iberian Peninsula in Europe. In AP US History context it is known for being one of major colonial powers in Americas during Age Of Discovery .Spanish encomienda system
: The encomienda system was established by Spain during their colonization period in Americas during 16th century. It allowed colonists to demand labor or tribute from indigenous people in exchange for providing protection and Christian education.St. Lawrence River
: The St. Lawrence River is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America, connecting the Great Lakes with the Atlantic Ocean.Tobacco
: A cash crop that was grown primarily in the Southern colonies of North America during the 17th and 18th centuries. It played a significant role in the economy of these colonies.Transatlantic exchanges
: The transatlantic exchanges refer to the transfer of people, goods, diseases, and ideas between the New World (Americas) and the Old World (Europe, Africa, Asia) following Christopher Columbus's voyage in 1492. This is also known as the Columbian Exchange.
Resources
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.