
7.9 Trait Theories of Personality
4 min read•december 22, 2022
Mary Valdez
John Mohl
Dalia Savy
Haseung Jun
Mary Valdez
John Mohl
Dalia Savy
Haseung Jun
Trait Theorists
Trait theorists believe that we can describe people's personalities by specifying their main characteristics 😎 These characteristics are thought to be stable and to motivate behavior with the specific trait. Trait theorists are most likely to claim that personality is genetic 🧬
Gordon Allport
Allport was the one that first described personality through traits, which are patterns of behavior.
cardinal traits - defining characteristic
central traits - general characteristics that form behavior
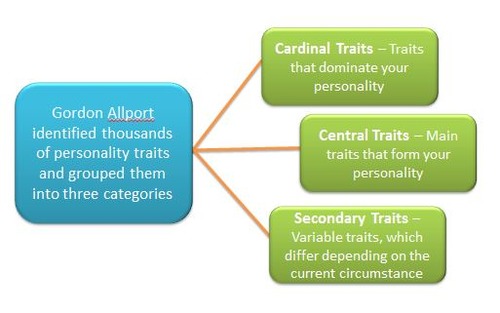
Image Courtesy of mollychandlerxx.
Factor analysis, from the intelligence unit, comes back here. It is a procedure used to find clusters of traits that are similar and make up your personality.
Every personality test that you take online is a trait personality test, and there are so many different types.
Hans Eysenck
Hans Eysenck is one who believes in the nomothetic approach: the belief that the same basic set of traits can be used to describe all people’s personalities 🌎He believed that by classifying all people along an introversion-extraversion scale and a stable-unstable scale, we could easily describe their personalities. Three dimensions played a key role: extroversion, neuroticism, and psychoticism. Extroversion means sociability and ability to pay attention to outside world and environment. Neuroticism measures our level of instability and psychoticism measures our level of tough-mindedness.
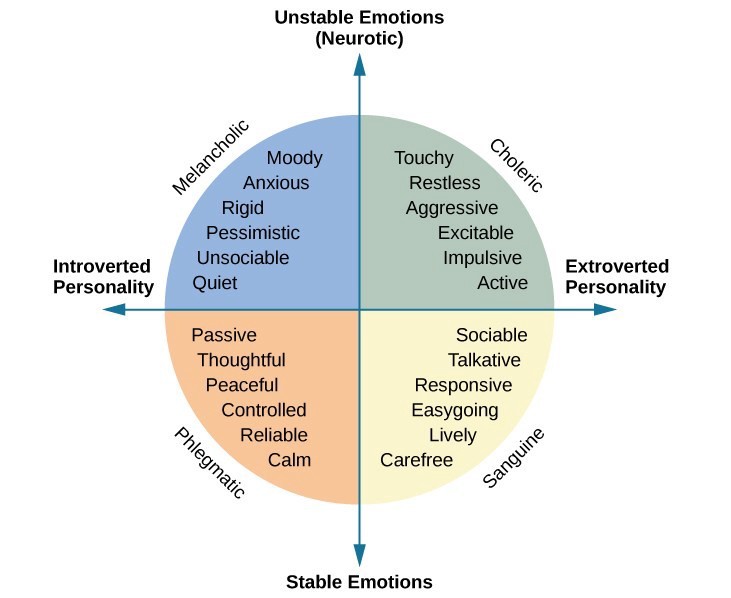
Image Courtesy of Medium.
Isabel Myers and Katharine Briggs
You could probably identify the type of personality test they created by their last names: the Myers-Brigg Type Indicator (MBTI). They mostly studied surface traits and source traits, which are visible areas of personality and underlying personality characteristics, respectively. It is used all around the world and there are four main sections of the test:
Favorite world
😊Extroverted—outgoing, energetic, sociable. Do you find yourself more attached to communicating with others?
🎨Introverted—gentle, quiet, caring, logical. Do you find yourself focused on yourself and being alone?
Information
🔰Sensing—organized, observant. Do you focus more on what is given to you?
🤔Intuition (N)—logical, conceptual, insightful. Do you interpret and add meaning to the information that is given to you?
Decisions
❤️Feeling type—sensitive, appreciative, tactful. Do you put more weight on personal concerns?
⚖️Thinking type—are good at analyzing pros and cons and are logical. Do you put more weight on facts and objective?
Structure
💭Judging—determined, concrete. Do you stay to what you know?
🔎Perceiving—independent, questioning, adaptable. Do you stay open to new things?
You don't really have to know the specifics, but it's really interesting to fit yourself into each category. Here's the link if you want to take the test and see if you guessed correctly. Have some fun with what you learn!
This information was adapted from the Myers-Brigg Website.
Here is a diagram of the different personality types that come from these four traits:

Image Courtesy of Mouth Foods.
Raymond Cattell
Cattell created the 16 PF (personality factor) which measures what he believed were the 16 basic traits present in all people, but to different degrees. It is unlikely that you have to know the 16 factors.
Paul Costa and Robert McCrea
Paul Costa & Robert McCrea proposed that personality can be described using the big five personality traits:
📆Openness—Do you like change? Can you adapt to it?
Low score: practical, prefers routine, comforting
High score: imaginative, prefers variety, independent
🧮Consciousness—Are you organized and careful?
Low score: disorganized, careless, impulsive
High score: organized, careful, disciplined
😊Agreeableness—How well do you get along with others?
Low score: ruthless, suspicious, uncooperative
High score: soft-hearted, trusting, helpful
🗣️Extroversion—Are you shy or outgoing?
Low score: retiring, sober, reserved
High score: sociable, affectionate, fun-loving
😬Neuroticism—Are you anxious often?
Low score: calm, secure, self-satisfied
High score: anxious, insecure, self-pitying
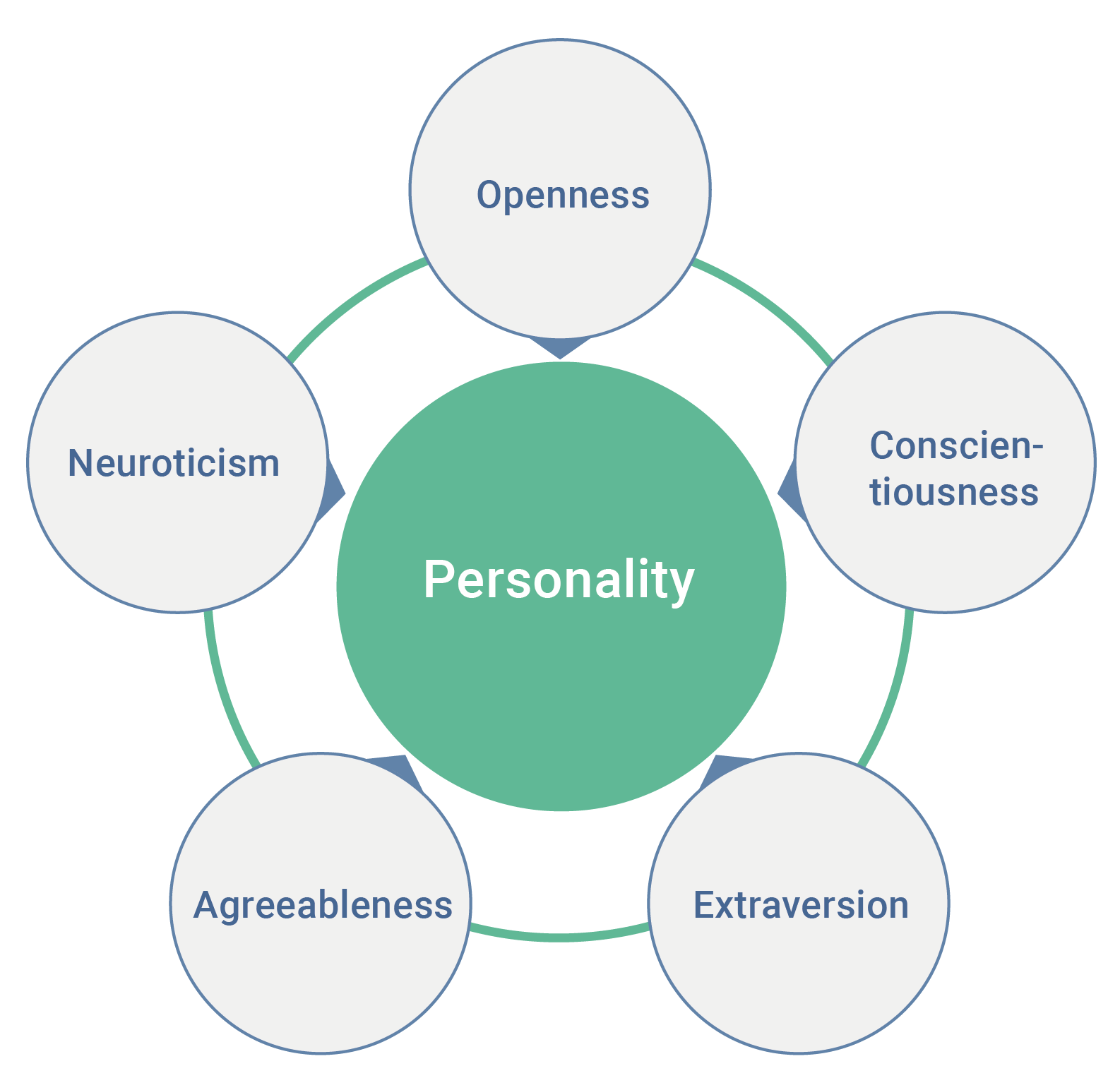
Image Courtesy of Wikipedia.
These five traits, unlike the past few types of personality tests, should be memorized. Use the mnemonic device "OCEAN" to help.
Comparing Personality Theories
To compare the personality theories you learned in the past few key topics, here is a nice table:
| Personality Theory | Key Proponents | Assumptions | View of Personality |
| Psychoanalytic | Freud | Emotional disorders spring from unconscious dynamics, such as unresolved sexual and other childhood conflicts, and fixation at various developmental stages. Defense mechanisms fend off anxiety. | Personality consists of pleasure-seeking impulses (the id), a reality-oriented executive (the ego), and an internalized set of ideals (the superego) |
| Psychodynamic | Adler, Horney, Jung | The unconscious and conscious minds interact. Childhood experiences and defense mechanisms are important. | The dynamic interplay of conscious and unconscious motives and conflicts shape our personality. |
| Humanistic | Rogers, Maslow | Rather than examining the struggles of sick people, it's better to focus on the ways healthy people strive for self-realization. | If our basic human needs are met, people will strive toward self-actualization. In a climate of unconditional positive regard, we can develop self-awareness and a more realistic and positive self-concept. |
| Trait | Allport, Eysenck, McCrae, Costa | We have certain stable and enduring characteristics, influenced by genetic predispositions. | Scientific study of traits has isolated important dimensions of personality, such as the Big Five traits. |
| Social-Cognitive | Bandura | Our traits and the social context interact to produce our behaviors. | Conditioning and observational learning interact with cognition to create behavior patterns. |
Table Courtesy of Propertarianism. All credit to David G. Myers and Nathan DeWall
🎥 Watch: AP Psychology—Personality Theories
🏆 Trivia—Personality, Motivation, and Emotion
Key Terms to Review (27)
16 PF (Personality Factor)
: The 16 Personality Factor questionnaire is a self-report personality test developed by Raymond Cattell. It measures an individual's 16 different primary traits to understand their complete personality profile.Agreeableness
: Agreeableness is another one of the five personality traits in the Big Five model. It reflects how cooperative, kind-hearted or antagonistic someone can be towards others.Big Five Personality Traits
: The Big Five Personality Traits are five broad dimensions used to describe human personality. These include openness to experience, conscientiousness, extraversion, introversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism.Cardinal Traits
: Cardinal traits are those that dominate an individual's whole life, often to the point that the person becomes known specifically for these traits.Central Traits
: These are the core traits that form the basis of an individual's personality. They are the handful of defining characteristics that can be used to describe a person.Consciousness
: Consciousness refers to our awareness of ourselves and our environment. It is a subjective experience of thoughts, feelings, and perceptions.Extroversion
: Extroversion is a personality trait characterized by outgoingness, high energy, and sociability. People with this trait tend to enjoy being around others, are often quite talkative, and generally feel energized by social interaction.Factor Analysis
: Factor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed variables in terms of fewer unobserved variables called factors. It helps identify clusters or groups of related items on psychological tests.Feeling Type
: In psychology, particularly in Carl Jung’s personality theory, the feeling type refers to individuals who make decisions based on emotions and values rather than objective facts.Gordon Allport
: Gordon Allport was an American psychologist who was one of the first to focus on the study of human personality and is often referred to as one of the founding figures of personality psychology.Hans Eysenck
: He was a German-British psychologist who proposed a model of personality based on three dimensions - extraversion/introversion, neuroticism/stability, and psychoticism/superego function.Intuition (N)
: Intuition is an unconscious process of acquiring knowledge or understanding without the conscious use of reasoning. It's a gut feeling or instinct that guides decision-making.Isabel Myers and Katharine Briggs
: Isabel Myers and Katharine Briggs were mother-daughter psychologists who developed the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI), a popular psychological tool used to measure how people perceive the world and make decisions.Judging
: In psychology, judging refers to the cognitive process of forming an opinion or evaluation by discerning and comparing. It's one of the four dimensions of personality identified in the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI).Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)
: The MBTI is a self-report questionnaire designed to identify a person's personality type, strengths, and preferences. It categorizes individuals into 16 different personality types.Neuroticism
: Neuroticism is a personality trait involving long-term tendency to be in a negative emotional state. Individuals with high levels of neuroticism tend to have mood swings, anxiety, irritability or sadness.Nomothetic Approach
: The nomothetic approach in psychology focuses on identifying general laws and trends that apply to large groups of people, rather than studying individual differences.Openness
: In psychology, openness refers to one of the five personality traits in the Big Five model. It represents a person's willingness to experience new things, their level of creativity, and their appreciation for art and beauty.Paul Costa and Robert McCrea
: Paul Costa and Robert McCrae are psychologists who developed the Five-Factor Model (FFM) or "Big Five" model of personality traits.Perceiving
: In psychology context, perceiving refers to how we interpret our sensory impressions to make sense of our environment. It's also one dimension in MBTI which indicates flexibility and spontaneity.Psychoticism
: Psychoticism is a personality trait associated with a tendency towards psychosis. It includes characteristics such as aggressiveness, impulsivity, aloofness, and antisocial behavior.Raymond Cattell
: Raymond Cattell was a British-American psychologist known for his exploration into areas like personality theory and psychometrics. He developed 16 Personality Factors theory that describes human personality traits.Sensing
: In psychology context, sensing refers to how we perceive physical stimuli from our environment through our five senses - sight, hearing, smell, taste and touch.Source Traits
: These are the foundational characteristics or driving forces behind our personalities. They're less obvious than surface traits but influence our attitudes and behaviors significantly.Surface Traits
: These are observable characteristics in a person's personality, which can be easily identified by other people.Thinking Type
: In Carl Jung’s personality theory, a thinking type refers to individuals who make decisions based on logical reasoning and objective analysis rather than personal values or emotions.Trait Theorists
: Trait theorists are psychologists who attempt to describe personality in terms of a person's traits, which are habitual patterns of behavior, thought, and emotion.7.9 Trait Theories of Personality
4 min read•december 22, 2022
Mary Valdez
John Mohl
Dalia Savy
Haseung Jun
Mary Valdez
John Mohl
Dalia Savy
Haseung Jun
Trait Theorists
Trait theorists believe that we can describe people's personalities by specifying their main characteristics 😎 These characteristics are thought to be stable and to motivate behavior with the specific trait. Trait theorists are most likely to claim that personality is genetic 🧬
Gordon Allport
Allport was the one that first described personality through traits, which are patterns of behavior.
cardinal traits - defining characteristic
central traits - general characteristics that form behavior

Image Courtesy of mollychandlerxx.
Factor analysis, from the intelligence unit, comes back here. It is a procedure used to find clusters of traits that are similar and make up your personality.
Every personality test that you take online is a trait personality test, and there are so many different types.
Hans Eysenck
Hans Eysenck is one who believes in the nomothetic approach: the belief that the same basic set of traits can be used to describe all people’s personalities 🌎He believed that by classifying all people along an introversion-extraversion scale and a stable-unstable scale, we could easily describe their personalities. Three dimensions played a key role: extroversion, neuroticism, and psychoticism. Extroversion means sociability and ability to pay attention to outside world and environment. Neuroticism measures our level of instability and psychoticism measures our level of tough-mindedness.

Image Courtesy of Medium.
Isabel Myers and Katharine Briggs
You could probably identify the type of personality test they created by their last names: the Myers-Brigg Type Indicator (MBTI). They mostly studied surface traits and source traits, which are visible areas of personality and underlying personality characteristics, respectively. It is used all around the world and there are four main sections of the test:
Favorite world
😊Extroverted—outgoing, energetic, sociable. Do you find yourself more attached to communicating with others?
🎨Introverted—gentle, quiet, caring, logical. Do you find yourself focused on yourself and being alone?
Information
🔰Sensing—organized, observant. Do you focus more on what is given to you?
🤔Intuition (N)—logical, conceptual, insightful. Do you interpret and add meaning to the information that is given to you?
Decisions
❤️Feeling type—sensitive, appreciative, tactful. Do you put more weight on personal concerns?
⚖️Thinking type—are good at analyzing pros and cons and are logical. Do you put more weight on facts and objective?
Structure
💭Judging—determined, concrete. Do you stay to what you know?
🔎Perceiving—independent, questioning, adaptable. Do you stay open to new things?
You don't really have to know the specifics, but it's really interesting to fit yourself into each category. Here's the link if you want to take the test and see if you guessed correctly. Have some fun with what you learn!
This information was adapted from the Myers-Brigg Website.
Here is a diagram of the different personality types that come from these four traits:

Image Courtesy of Mouth Foods.
Raymond Cattell
Cattell created the 16 PF (personality factor) which measures what he believed were the 16 basic traits present in all people, but to different degrees. It is unlikely that you have to know the 16 factors.
Paul Costa and Robert McCrea
Paul Costa & Robert McCrea proposed that personality can be described using the big five personality traits:
📆Openness—Do you like change? Can you adapt to it?
Low score: practical, prefers routine, comforting
High score: imaginative, prefers variety, independent
🧮Consciousness—Are you organized and careful?
Low score: disorganized, careless, impulsive
High score: organized, careful, disciplined
😊Agreeableness—How well do you get along with others?
Low score: ruthless, suspicious, uncooperative
High score: soft-hearted, trusting, helpful
🗣️Extroversion—Are you shy or outgoing?
Low score: retiring, sober, reserved
High score: sociable, affectionate, fun-loving
😬Neuroticism—Are you anxious often?
Low score: calm, secure, self-satisfied
High score: anxious, insecure, self-pitying

Image Courtesy of Wikipedia.
These five traits, unlike the past few types of personality tests, should be memorized. Use the mnemonic device "OCEAN" to help.
Comparing Personality Theories
To compare the personality theories you learned in the past few key topics, here is a nice table:
| Personality Theory | Key Proponents | Assumptions | View of Personality |
| Psychoanalytic | Freud | Emotional disorders spring from unconscious dynamics, such as unresolved sexual and other childhood conflicts, and fixation at various developmental stages. Defense mechanisms fend off anxiety. | Personality consists of pleasure-seeking impulses (the id), a reality-oriented executive (the ego), and an internalized set of ideals (the superego) |
| Psychodynamic | Adler, Horney, Jung | The unconscious and conscious minds interact. Childhood experiences and defense mechanisms are important. | The dynamic interplay of conscious and unconscious motives and conflicts shape our personality. |
| Humanistic | Rogers, Maslow | Rather than examining the struggles of sick people, it's better to focus on the ways healthy people strive for self-realization. | If our basic human needs are met, people will strive toward self-actualization. In a climate of unconditional positive regard, we can develop self-awareness and a more realistic and positive self-concept. |
| Trait | Allport, Eysenck, McCrae, Costa | We have certain stable and enduring characteristics, influenced by genetic predispositions. | Scientific study of traits has isolated important dimensions of personality, such as the Big Five traits. |
| Social-Cognitive | Bandura | Our traits and the social context interact to produce our behaviors. | Conditioning and observational learning interact with cognition to create behavior patterns. |
Table Courtesy of Propertarianism. All credit to David G. Myers and Nathan DeWall
🎥 Watch: AP Psychology—Personality Theories
🏆 Trivia—Personality, Motivation, and Emotion
Key Terms to Review (27)
16 PF (Personality Factor)
: The 16 Personality Factor questionnaire is a self-report personality test developed by Raymond Cattell. It measures an individual's 16 different primary traits to understand their complete personality profile.Agreeableness
: Agreeableness is another one of the five personality traits in the Big Five model. It reflects how cooperative, kind-hearted or antagonistic someone can be towards others.Big Five Personality Traits
: The Big Five Personality Traits are five broad dimensions used to describe human personality. These include openness to experience, conscientiousness, extraversion, introversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism.Cardinal Traits
: Cardinal traits are those that dominate an individual's whole life, often to the point that the person becomes known specifically for these traits.Central Traits
: These are the core traits that form the basis of an individual's personality. They are the handful of defining characteristics that can be used to describe a person.Consciousness
: Consciousness refers to our awareness of ourselves and our environment. It is a subjective experience of thoughts, feelings, and perceptions.Extroversion
: Extroversion is a personality trait characterized by outgoingness, high energy, and sociability. People with this trait tend to enjoy being around others, are often quite talkative, and generally feel energized by social interaction.Factor Analysis
: Factor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed variables in terms of fewer unobserved variables called factors. It helps identify clusters or groups of related items on psychological tests.Feeling Type
: In psychology, particularly in Carl Jung’s personality theory, the feeling type refers to individuals who make decisions based on emotions and values rather than objective facts.Gordon Allport
: Gordon Allport was an American psychologist who was one of the first to focus on the study of human personality and is often referred to as one of the founding figures of personality psychology.Hans Eysenck
: He was a German-British psychologist who proposed a model of personality based on three dimensions - extraversion/introversion, neuroticism/stability, and psychoticism/superego function.Intuition (N)
: Intuition is an unconscious process of acquiring knowledge or understanding without the conscious use of reasoning. It's a gut feeling or instinct that guides decision-making.Isabel Myers and Katharine Briggs
: Isabel Myers and Katharine Briggs were mother-daughter psychologists who developed the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI), a popular psychological tool used to measure how people perceive the world and make decisions.Judging
: In psychology, judging refers to the cognitive process of forming an opinion or evaluation by discerning and comparing. It's one of the four dimensions of personality identified in the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI).Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)
: The MBTI is a self-report questionnaire designed to identify a person's personality type, strengths, and preferences. It categorizes individuals into 16 different personality types.Neuroticism
: Neuroticism is a personality trait involving long-term tendency to be in a negative emotional state. Individuals with high levels of neuroticism tend to have mood swings, anxiety, irritability or sadness.Nomothetic Approach
: The nomothetic approach in psychology focuses on identifying general laws and trends that apply to large groups of people, rather than studying individual differences.Openness
: In psychology, openness refers to one of the five personality traits in the Big Five model. It represents a person's willingness to experience new things, their level of creativity, and their appreciation for art and beauty.Paul Costa and Robert McCrea
: Paul Costa and Robert McCrae are psychologists who developed the Five-Factor Model (FFM) or "Big Five" model of personality traits.Perceiving
: In psychology context, perceiving refers to how we interpret our sensory impressions to make sense of our environment. It's also one dimension in MBTI which indicates flexibility and spontaneity.Psychoticism
: Psychoticism is a personality trait associated with a tendency towards psychosis. It includes characteristics such as aggressiveness, impulsivity, aloofness, and antisocial behavior.Raymond Cattell
: Raymond Cattell was a British-American psychologist known for his exploration into areas like personality theory and psychometrics. He developed 16 Personality Factors theory that describes human personality traits.Sensing
: In psychology context, sensing refers to how we perceive physical stimuli from our environment through our five senses - sight, hearing, smell, taste and touch.Source Traits
: These are the foundational characteristics or driving forces behind our personalities. They're less obvious than surface traits but influence our attitudes and behaviors significantly.Surface Traits
: These are observable characteristics in a person's personality, which can be easily identified by other people.Thinking Type
: In Carl Jung’s personality theory, a thinking type refers to individuals who make decisions based on logical reasoning and objective analysis rather than personal values or emotions.Trait Theorists
: Trait theorists are psychologists who attempt to describe personality in terms of a person's traits, which are habitual patterns of behavior, thought, and emotion.
Resources
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.