
8.8 World War II
6 min read•january 29, 2023
Jillian Holbrook
Jillian Holbrook
Causes of WWII
Tensions were mounting from the moment of the signing of the in 1919 to the invasion of . Extreme economic conditions left many Europeans desperate for change, no matter what that change looked like.
The Weimer Republic
Beyond the economic stress of the 1919, one of the stipulations required that Germany, formerly a monarchy, become a democracy. This first weak run of German democracy was the . The consisted of ineffectual government strategies and failure to thrive under pressure from the Allied Powers who enforced the and the authoritarian politicians whose silver tongues promised bright futures for the German Republic.
It wasn't entirely the fault of its leaders that the failed; there was virtually no support from the German people for the democratic government as it stood. The German people were already disheartened by the perceived betrayal of when he surrendered to the Allied Powers on November 11, 1919 (now known as armistice day). When authoritarian leaders began promising changes -- to break from economic stress, grow the economy, boost morale, and create a great nation -- they were all voted into office.
Violations of the Treaty of Versailles
violated the with his land claims in and and . remilitarization of the . However, these egregious violations were overlooked by Britain and due to fears of starting another global war.
Ultimately, the immediate cause of WWII was the German and Soviet invasion of . had been defined and protected by the . Yet there was no real force behind the , meaning Hitler and Stalin were not intimidated.
The European Theatre
Germany was the first to invade . Only 16 days later, the joined them. Both were upset with the lands they had lost in the with the creation of , so they sought to reclaim that land.
and declared war on Germany but not the . Both knew that they would eventually need the to defeat Germany. To justify this, painted the German invasion of as a break in the , violence toward Polish people, and a serious territorial concern.
Military Methods
Fighting styles and weaponry were similar to WWI, with the exception of some upgrades and developments:
Modes of transportation such as vehicles, new ships, aircraft
Communication technology
Guided missiles and ballistic missiles
New medicines and surgical techniques
Atomic weapons
German -- all-out warfare known as "lightning" warfare
WWII saw German expansion deeper into allied territory than in WWI. Hitler was able to assert his control across northern Europe, with the exception of the and . His allies controlled nearly all of southern Europe with the exception of , , and . However, Hitler and had both received aid from in and used his land as training grounds for their soldiers.
Allied invasions of began in 1943. After taking the island of , US and Allied forces used it as a base to mount a successful attack on . was forced to resign from his dictatorial rule of and imprisoned. Secret negotiations began with the provisional government to work on removing German troops from .
The major turning point of the was the on June 6, 1944. The United States organized a mass naval invasion of (just north of ), stormed the German beachhead there, and used this invasion as a means of marching on . The Allied forces retook and the country of , then began pushing into .
In April of 1945, Hitler committed suicide, and the Allies began liberating the remainder of German-occupied areas and .
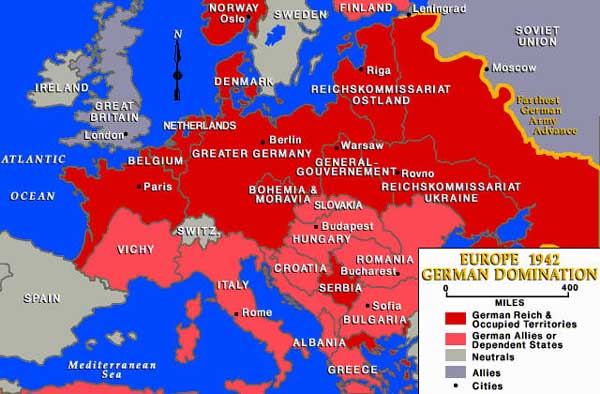
Map of the European theater. Photo courtesy of Jewish Virtual Library.
In the east, Germany moved into Soviet territory. The Soviets struggled with their new , failing to produce enough food, ammunition, or weaponry for their population. However, they were prepared when the Germans marched toward . Over a million Soviet soldiers held off the Germans, and as the Germans ran out of food and supplies, they were forced to surrender. This was the turning point of the Eastern Front.
Middle Eastern / African Theatre
had plans to rebuild the former Roman Empire under fascist rule. Germans sent troops to aid the Italian invasions of and . From there, they moved to . The Germans planned to take , move through the Middle East, and attack the from the south. However, they were met with Allied forces, and over the course of three years, Allied powers eventually prevailed.
By 1944, the Germans were engaged in battles with the French, the British, , the , and US Forces in all of the above locations. Fighting a multi-front war eventually began to weigh on the German military and supply line. With their forces split for the majority of the war, they were unable to fully focus on any front and began losing ground. After the Allied invasion of , and the Middle East were lost to the Axis powers.
Pacific Theatre
The of 1868 in Japan ended a period of isolation after the was overthrown. This new regime sought to introduce Japan to the changes of the developed world, but to do so, they needed resources. The only way to obtain them, being from a mountainous archipelago, was to expand their territory.
Japan had successful invasions of , , and the against the . Through this, they obtained the use of key ports and essential resources such as coal, petroleum, iron, and more. They could have traded but wanted a monopoly, so they used war to achieve control.
The Japanese invasion of in 1931 prompted a response from the US and the . Japan removed itself as a member of the and violated the , a free trade policy between the US and . They also committed mass atrocities, such as the in 1937. The US placed harsh economic sanctions on Japan, which only made them want to stand stronger and push further into . After failed negotiations, war seemed inevitable to the Japanese, and they bombed the US Pacific naval fleet at , on December 7, 1941.
This set off a series of military engagements between the US and Japan. The attack at Pearl Harbor was successful, but not as successful as it could have been due to training exercises that kept many ships at sea. The most immediate attack by the United States was a firebombing of Tokyo in April of 1942, but the most significant was the later that year. US forces began a series of to keep Japan from its expansionist goals.
This theatre ended with the US attempting to force surrender from Japan through a threat of invasion. However, this tactic did not work. On August 6th and 9th, 1945, President Truman made decisions to drop atomic bombs on the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Japan surrendered in the days after.
Key Terms to Review (47)
Adolf Hitler
: Adolf Hitler was a German politician and leader of the Nazi Party who rose to power as Chancellor of Germany in 1933, and later Führer in 1934, ruling Germany during World War II until his suicide in 1945.Austria
: Austria is a landlocked East Alpine country located in Central Europe. Historically, it was one of Europe's major powers, particularly during Habsburg rule which lasted several centuries.Battle of Midway
: The Battle of Midway was a decisive naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II that took place between June 4 and June 7, 1942. It was here that American forces successfully defeated an attacking fleet of the Imperial Japanese Navy.Belgium
: A small country located in Western Europe known for its medieval towns and Renaissance architecture. It played a key role in both World Wars.Blitzkrieg
: A German term meaning "lightning war". It's a military strategy used by Germany during World War II that aimed at quick victories through fast, concentrated attacks intended to create disorganization among enemy forces.China
: In the context of AP European History, China refers to a major Eastern civilization that has had significant influence on global trade, culture, and politics. It's known for its dynastic rule, technological advancements like gunpowder and printing, and philosophies such as Confucianism.Concentration camps
: Places where large numbers of people are kept as prisoners under armed guard during wartime; these were notably used by Nazis during World War II for genocide against Jews and other groups they deemed undesirable.Czechoslovakia
: Czechoslovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe that existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until its peaceful dissolution into the Czech Republic and Slovakia on January 1, 1993.D-Day Invasion
: The D-Day Invasion, also known as the Normandy landings, was a significant military operation during World War II where Allied forces launched an amphibious invasion on the beaches of Normandy, France on June 6, 1944. This marked the beginning of the end for Nazi Germany.European Theatre
: The European Theatre refers to a large area where significant military operations took place during World War II across Europe against Nazi Germany and its allies.Five Year Plans
: These were government plans in the Soviet Union, initiated by Stalin, for economic goals over periods of five years. They aimed at rapid industrialization and collectivization with ambitious targets that often led to widespread hardship.France
: France is a country located in Western Europe. Known for its cultural influence, it has played a central role in European history from the French Revolution to both World Wars.Francisco Franco
: Francisco Franco was a Spanish general who ruled over Spain as a military dictator from 1939 until his death in 1975.Great Britain
: Great Britain is an island located off Northwestern Europe which includes England, Scotland, and Wales. It has played a significant role in global history due to its extensive empire and influence on world politics, culture, and economy.Greece
: In the context of AP European History, Greece refers to its role during World War II. It was invaded by Italy and later Germany, leading to occupation until 1944.Island Hopping
: Island hopping is a military strategy used by Allies against Japan during World War II. It involved selectively attacking specific enemy-held islands and bypassing others to reach Japan quickly.Italy
: Italy, in the context of AP European History, refers to a country located in Southern Europe that became a unified nation-state in 1861. Prior to this, it was a collection of independent city-states and kingdoms.Kaiser Wilhelm II
: Kaiser Wilhelm II was the last German Emperor and King of Prussia who ruled from 1888 until his abdication at the end of World War I in 1918. His policies contributed significantly to tensions leading up to World War I.Korean Peninsula
: The Korean Peninsula is located in East Asia extending southwards for about 1,100 km (680 miles) from continental Asia into the Pacific Ocean; divided into two countries North Korea and South Korea after World War II.League of Nations
: An international organization established after World War I under the provisions of the Treaty of Versailles. Its goal was to promote world peace by encouraging diplomatic negotiation and disarmament.Manchuria
: Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia. It was a significant battleground during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with Russia, Japan, and China all vying for control.Meiji Restoration
: The Meiji Restoration was a political revolution in Japan that ended the Tokugawa shogunate and restored practical imperial rule to Japan under Emperor Meiji in 1868.Middle Eastern / African Theatre
: The Middle Eastern/African Theatre refers to military operations that took place in North Africa and the Middle East during World War II. It involved many nations including Britain, Italy, France, Germany, and later America.Mussolini
: Benito Mussolini was an Italian political leader who became the fascist dictator of Italy from 1925 to 1945.Nanjing Massacre
: The Nanjing Massacre was a mass murder and mass rape committed by Japanese troops against the residents of Nanjing, then the capital of China, during the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937-38.Normandy, France
: Normandy is a region located in northern France along the English Channel. It is historically significant because it was here that Allied forces landed during D-Day in World War II.North Africa
: North Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. It includes countries like Egypt, Libya, Algeria, Tunisia and Morocco. This region played significant roles during both World Wars due to its strategic location.Open Door Policy
: The Open Door Policy refers to America’s approach to China around 1900, allowing multiple imperial powers access to China—with none having exclusive control over Chinese trade or territory.Pacific Theatre
: The Pacific Theatre refers to the area of operations in the Pacific Ocean and its surrounding areas during World War II. It was a major theatre of war between the Allies and Japan.Paris
: Paris is the capital city of France and a global hub for art, fashion, gastronomy and culture. It's known for its many iconic landmarks like Eiffel Tower, Louvre Museum and Notre-Dame cathedral.Pearl Harbor, Hawaii
: Pearl Harbor is a U.S. naval base near Honolulu, Hawaii, that was the scene of a devastating surprise attack by Japanese forces on December 7, 1941.Poland
: Poland is a country located in Central Europe known for its rich history which includes periods of great prosperity interspersed with devastating invasions.Portugal
: A Southern European country located on the Iberian Peninsula. It's known for its maritime explorations during the Age of Discovery which made it a global empire in the 15th-16th centuries.Rhineland
: The Rhineland is a region in western Germany that borders Belgium, France, and the Netherlands. It was a key strategic location during both World Wars due to its industrial capacity and geographical position.Rome
: Rome is the capital city of Italy and was once at the heart of the Roman Empire. Known as "The Eternal City", it's famous for its ancient ruins such as Colosseum and Forum as well as Vatican City.Russians
: Russians are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. They are the most numerous ethnic group in Europe.Sicily
: Sicily is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea and an autonomous region of Italy. It has a rich history due to its strategic location, with various civilizations ruling it over time.Soviet Union
: The Soviet Union was a federal socialist state that existed from 1922 to 1991. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party with Moscow as its capital in its largest republic, Russian SFSR.Spain
: Spain is a country located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. It has played a significant role in European history, particularly during the Age of Exploration and the Spanish Civil War.Stalingrad
: Stalingrad was a major battle of World War II in which Nazi Germany and its allies fought the Soviet Union for control of the city of Stalingrad (now Volgograd) in Southern Russia.Sweden
: A Scandinavian nation in Northern Europe, known for its high standard of living and strong welfare state. It played a significant role in European history, particularly during the 17th century when it was a major power.Switzerland
: A landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Europe. Known for its political neutrality, direct democracy, and high standard of living.Tokugawa Shogunate
: The Tokugawa Shogunate was a feudal regime ruled by Shogun Tokugawa Ieyasu established in Edo (now Tokyo) which lasted from 1603 until 1868.Treaty of Versailles
: The Treaty of Versailles was signed on June 28, 1919, ending World War I. The treaty held Germany responsible for starting the war and imposed heavy penalties on them.United Kingdom
: A country located off the northwestern coast of mainland Europe. The UK is a union of four countries: England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. It has been a major player in global politics and economics.Weimar Republic
: The Weimar Republic was Germany's government from 1919 to 1933, a period marked by political instability, economic volatility, and social change. It ended with Adolf Hitler's rise to power.Yugoslavia
: Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast Europe during most of the 20th century. It came into existence after World War I in 1918 under the name of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes by union of the South Slavic regions. After World War II, it became a socialist federation known as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.8.8 World War II
6 min read•january 29, 2023
Jillian Holbrook
Jillian Holbrook
Causes of WWII
Tensions were mounting from the moment of the signing of the in 1919 to the invasion of . Extreme economic conditions left many Europeans desperate for change, no matter what that change looked like.
The Weimer Republic
Beyond the economic stress of the 1919, one of the stipulations required that Germany, formerly a monarchy, become a democracy. This first weak run of German democracy was the . The consisted of ineffectual government strategies and failure to thrive under pressure from the Allied Powers who enforced the and the authoritarian politicians whose silver tongues promised bright futures for the German Republic.
It wasn't entirely the fault of its leaders that the failed; there was virtually no support from the German people for the democratic government as it stood. The German people were already disheartened by the perceived betrayal of when he surrendered to the Allied Powers on November 11, 1919 (now known as armistice day). When authoritarian leaders began promising changes -- to break from economic stress, grow the economy, boost morale, and create a great nation -- they were all voted into office.
Violations of the Treaty of Versailles
violated the with his land claims in and and . remilitarization of the . However, these egregious violations were overlooked by Britain and due to fears of starting another global war.
Ultimately, the immediate cause of WWII was the German and Soviet invasion of . had been defined and protected by the . Yet there was no real force behind the , meaning Hitler and Stalin were not intimidated.
The European Theatre
Germany was the first to invade . Only 16 days later, the joined them. Both were upset with the lands they had lost in the with the creation of , so they sought to reclaim that land.
and declared war on Germany but not the . Both knew that they would eventually need the to defeat Germany. To justify this, painted the German invasion of as a break in the , violence toward Polish people, and a serious territorial concern.
Military Methods
Fighting styles and weaponry were similar to WWI, with the exception of some upgrades and developments:
Modes of transportation such as vehicles, new ships, aircraft
Communication technology
Guided missiles and ballistic missiles
New medicines and surgical techniques
Atomic weapons
German -- all-out warfare known as "lightning" warfare
WWII saw German expansion deeper into allied territory than in WWI. Hitler was able to assert his control across northern Europe, with the exception of the and . His allies controlled nearly all of southern Europe with the exception of , , and . However, Hitler and had both received aid from in and used his land as training grounds for their soldiers.
Allied invasions of began in 1943. After taking the island of , US and Allied forces used it as a base to mount a successful attack on . was forced to resign from his dictatorial rule of and imprisoned. Secret negotiations began with the provisional government to work on removing German troops from .
The major turning point of the was the on June 6, 1944. The United States organized a mass naval invasion of (just north of ), stormed the German beachhead there, and used this invasion as a means of marching on . The Allied forces retook and the country of , then began pushing into .
In April of 1945, Hitler committed suicide, and the Allies began liberating the remainder of German-occupied areas and .

Map of the European theater. Photo courtesy of Jewish Virtual Library.
In the east, Germany moved into Soviet territory. The Soviets struggled with their new , failing to produce enough food, ammunition, or weaponry for their population. However, they were prepared when the Germans marched toward . Over a million Soviet soldiers held off the Germans, and as the Germans ran out of food and supplies, they were forced to surrender. This was the turning point of the Eastern Front.
Middle Eastern / African Theatre
had plans to rebuild the former Roman Empire under fascist rule. Germans sent troops to aid the Italian invasions of and . From there, they moved to . The Germans planned to take , move through the Middle East, and attack the from the south. However, they were met with Allied forces, and over the course of three years, Allied powers eventually prevailed.
By 1944, the Germans were engaged in battles with the French, the British, , the , and US Forces in all of the above locations. Fighting a multi-front war eventually began to weigh on the German military and supply line. With their forces split for the majority of the war, they were unable to fully focus on any front and began losing ground. After the Allied invasion of , and the Middle East were lost to the Axis powers.
Pacific Theatre
The of 1868 in Japan ended a period of isolation after the was overthrown. This new regime sought to introduce Japan to the changes of the developed world, but to do so, they needed resources. The only way to obtain them, being from a mountainous archipelago, was to expand their territory.
Japan had successful invasions of , , and the against the . Through this, they obtained the use of key ports and essential resources such as coal, petroleum, iron, and more. They could have traded but wanted a monopoly, so they used war to achieve control.
The Japanese invasion of in 1931 prompted a response from the US and the . Japan removed itself as a member of the and violated the , a free trade policy between the US and . They also committed mass atrocities, such as the in 1937. The US placed harsh economic sanctions on Japan, which only made them want to stand stronger and push further into . After failed negotiations, war seemed inevitable to the Japanese, and they bombed the US Pacific naval fleet at , on December 7, 1941.
This set off a series of military engagements between the US and Japan. The attack at Pearl Harbor was successful, but not as successful as it could have been due to training exercises that kept many ships at sea. The most immediate attack by the United States was a firebombing of Tokyo in April of 1942, but the most significant was the later that year. US forces began a series of to keep Japan from its expansionist goals.
This theatre ended with the US attempting to force surrender from Japan through a threat of invasion. However, this tactic did not work. On August 6th and 9th, 1945, President Truman made decisions to drop atomic bombs on the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Japan surrendered in the days after.
Key Terms to Review (47)
Adolf Hitler
: Adolf Hitler was a German politician and leader of the Nazi Party who rose to power as Chancellor of Germany in 1933, and later Führer in 1934, ruling Germany during World War II until his suicide in 1945.Austria
: Austria is a landlocked East Alpine country located in Central Europe. Historically, it was one of Europe's major powers, particularly during Habsburg rule which lasted several centuries.Battle of Midway
: The Battle of Midway was a decisive naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II that took place between June 4 and June 7, 1942. It was here that American forces successfully defeated an attacking fleet of the Imperial Japanese Navy.Belgium
: A small country located in Western Europe known for its medieval towns and Renaissance architecture. It played a key role in both World Wars.Blitzkrieg
: A German term meaning "lightning war". It's a military strategy used by Germany during World War II that aimed at quick victories through fast, concentrated attacks intended to create disorganization among enemy forces.China
: In the context of AP European History, China refers to a major Eastern civilization that has had significant influence on global trade, culture, and politics. It's known for its dynastic rule, technological advancements like gunpowder and printing, and philosophies such as Confucianism.Concentration camps
: Places where large numbers of people are kept as prisoners under armed guard during wartime; these were notably used by Nazis during World War II for genocide against Jews and other groups they deemed undesirable.Czechoslovakia
: Czechoslovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe that existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until its peaceful dissolution into the Czech Republic and Slovakia on January 1, 1993.D-Day Invasion
: The D-Day Invasion, also known as the Normandy landings, was a significant military operation during World War II where Allied forces launched an amphibious invasion on the beaches of Normandy, France on June 6, 1944. This marked the beginning of the end for Nazi Germany.European Theatre
: The European Theatre refers to a large area where significant military operations took place during World War II across Europe against Nazi Germany and its allies.Five Year Plans
: These were government plans in the Soviet Union, initiated by Stalin, for economic goals over periods of five years. They aimed at rapid industrialization and collectivization with ambitious targets that often led to widespread hardship.France
: France is a country located in Western Europe. Known for its cultural influence, it has played a central role in European history from the French Revolution to both World Wars.Francisco Franco
: Francisco Franco was a Spanish general who ruled over Spain as a military dictator from 1939 until his death in 1975.Great Britain
: Great Britain is an island located off Northwestern Europe which includes England, Scotland, and Wales. It has played a significant role in global history due to its extensive empire and influence on world politics, culture, and economy.Greece
: In the context of AP European History, Greece refers to its role during World War II. It was invaded by Italy and later Germany, leading to occupation until 1944.Island Hopping
: Island hopping is a military strategy used by Allies against Japan during World War II. It involved selectively attacking specific enemy-held islands and bypassing others to reach Japan quickly.Italy
: Italy, in the context of AP European History, refers to a country located in Southern Europe that became a unified nation-state in 1861. Prior to this, it was a collection of independent city-states and kingdoms.Kaiser Wilhelm II
: Kaiser Wilhelm II was the last German Emperor and King of Prussia who ruled from 1888 until his abdication at the end of World War I in 1918. His policies contributed significantly to tensions leading up to World War I.Korean Peninsula
: The Korean Peninsula is located in East Asia extending southwards for about 1,100 km (680 miles) from continental Asia into the Pacific Ocean; divided into two countries North Korea and South Korea after World War II.League of Nations
: An international organization established after World War I under the provisions of the Treaty of Versailles. Its goal was to promote world peace by encouraging diplomatic negotiation and disarmament.Manchuria
: Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia. It was a significant battleground during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with Russia, Japan, and China all vying for control.Meiji Restoration
: The Meiji Restoration was a political revolution in Japan that ended the Tokugawa shogunate and restored practical imperial rule to Japan under Emperor Meiji in 1868.Middle Eastern / African Theatre
: The Middle Eastern/African Theatre refers to military operations that took place in North Africa and the Middle East during World War II. It involved many nations including Britain, Italy, France, Germany, and later America.Mussolini
: Benito Mussolini was an Italian political leader who became the fascist dictator of Italy from 1925 to 1945.Nanjing Massacre
: The Nanjing Massacre was a mass murder and mass rape committed by Japanese troops against the residents of Nanjing, then the capital of China, during the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937-38.Normandy, France
: Normandy is a region located in northern France along the English Channel. It is historically significant because it was here that Allied forces landed during D-Day in World War II.North Africa
: North Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. It includes countries like Egypt, Libya, Algeria, Tunisia and Morocco. This region played significant roles during both World Wars due to its strategic location.Open Door Policy
: The Open Door Policy refers to America’s approach to China around 1900, allowing multiple imperial powers access to China—with none having exclusive control over Chinese trade or territory.Pacific Theatre
: The Pacific Theatre refers to the area of operations in the Pacific Ocean and its surrounding areas during World War II. It was a major theatre of war between the Allies and Japan.Paris
: Paris is the capital city of France and a global hub for art, fashion, gastronomy and culture. It's known for its many iconic landmarks like Eiffel Tower, Louvre Museum and Notre-Dame cathedral.Pearl Harbor, Hawaii
: Pearl Harbor is a U.S. naval base near Honolulu, Hawaii, that was the scene of a devastating surprise attack by Japanese forces on December 7, 1941.Poland
: Poland is a country located in Central Europe known for its rich history which includes periods of great prosperity interspersed with devastating invasions.Portugal
: A Southern European country located on the Iberian Peninsula. It's known for its maritime explorations during the Age of Discovery which made it a global empire in the 15th-16th centuries.Rhineland
: The Rhineland is a region in western Germany that borders Belgium, France, and the Netherlands. It was a key strategic location during both World Wars due to its industrial capacity and geographical position.Rome
: Rome is the capital city of Italy and was once at the heart of the Roman Empire. Known as "The Eternal City", it's famous for its ancient ruins such as Colosseum and Forum as well as Vatican City.Russians
: Russians are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. They are the most numerous ethnic group in Europe.Sicily
: Sicily is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea and an autonomous region of Italy. It has a rich history due to its strategic location, with various civilizations ruling it over time.Soviet Union
: The Soviet Union was a federal socialist state that existed from 1922 to 1991. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party with Moscow as its capital in its largest republic, Russian SFSR.Spain
: Spain is a country located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. It has played a significant role in European history, particularly during the Age of Exploration and the Spanish Civil War.Stalingrad
: Stalingrad was a major battle of World War II in which Nazi Germany and its allies fought the Soviet Union for control of the city of Stalingrad (now Volgograd) in Southern Russia.Sweden
: A Scandinavian nation in Northern Europe, known for its high standard of living and strong welfare state. It played a significant role in European history, particularly during the 17th century when it was a major power.Switzerland
: A landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Europe. Known for its political neutrality, direct democracy, and high standard of living.Tokugawa Shogunate
: The Tokugawa Shogunate was a feudal regime ruled by Shogun Tokugawa Ieyasu established in Edo (now Tokyo) which lasted from 1603 until 1868.Treaty of Versailles
: The Treaty of Versailles was signed on June 28, 1919, ending World War I. The treaty held Germany responsible for starting the war and imposed heavy penalties on them.United Kingdom
: A country located off the northwestern coast of mainland Europe. The UK is a union of four countries: England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. It has been a major player in global politics and economics.Weimar Republic
: The Weimar Republic was Germany's government from 1919 to 1933, a period marked by political instability, economic volatility, and social change. It ended with Adolf Hitler's rise to power.Yugoslavia
: Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast Europe during most of the 20th century. It came into existence after World War I in 1918 under the name of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes by union of the South Slavic regions. After World War II, it became a socialist federation known as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.
Resources
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.