
1.3 Northern Renaissance
3 min read•january 7, 2023
Christine Lin
Isabela Padilha Vilela
Christine Lin
Isabela Padilha Vilela
The Northern Renaissance
The occurred after the Italian Renaissance, in the beginning of the 15th century. It affected northern countries in Europe such as , , , and the .
The and its scholars were a catalyst for the , in part because they began reading the original ⛪ and recognized discrepancies between those readings and the . Those in the were from diverse backgrounds and were passionate about religious reform, unlike those in the Italian Renaissance.
The biggest societal change during the was the invention of the by . The 🖶 with moveable type was created in during the 15th century. This invention led to the ability for the Church, northern humanists, and statesmen to spread their ideas and viewpoints to a wider audience and books on religion as well.
The is characterized by the idea of Christian Humanism 🧍♀️in which the teachings of Christianity were shaped to incorporate the meaning of the individual (what is it to be human?) in their studies. The "prince of humanism" was , a Dutch humanist and scholar that wrote several criticisms to the imposition of power and corruption of the Catholic Church. But, he was still a devout Christian and committed to the church. His version of the "" shaped modern biblical scholarship.
🎥 Watch: AP Euro - Northern Renaissance
The impact of the Northern Renaissance
The , with the new values in and individualism that challenge religious, political and intellectual institutions, focused heavily on religious reforms. As arose, religious reform and the creation of new religious sectors away from the Catholic Church was promoted.
The most important part of the is the printing press. As mentioned before, it led to an increase in literacy, which led to individuals beginning to question religious text and in turn, led to the demand for religious reform across northern Europe.
Italian Renaissance vs. Northern Renaissance
Italian Renaissance:
Heavily emphasized on the teaching of 📖
Less detailed depictions in art of everyday life “” and more mythological deceptions
Linked less on Religious issues, but more in intellectual reforms in history, literature and human anatomy
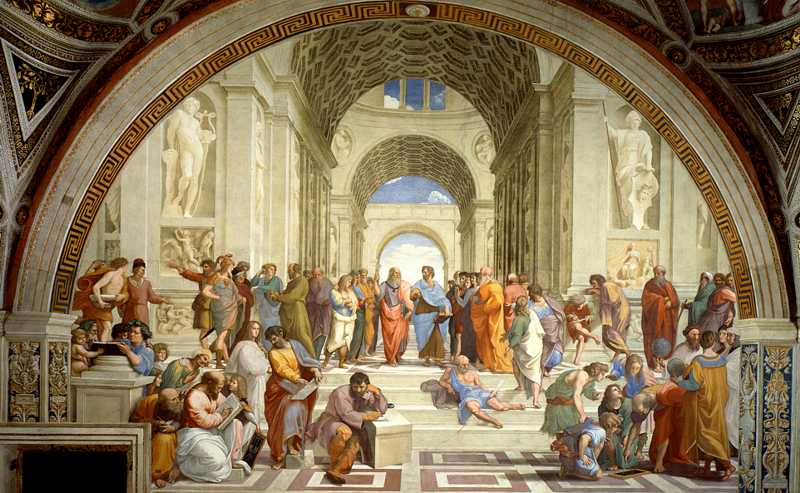

Image Courtesy of Artyfactory
Northern Renaissance:
Studied less on Classical texts
More domestic and religious depictions in art🎨 and everyday life (in greater detail)
Linked more with religious issues and reforms (the religious reforms that challenged and questioned❔ the practices of the Church)
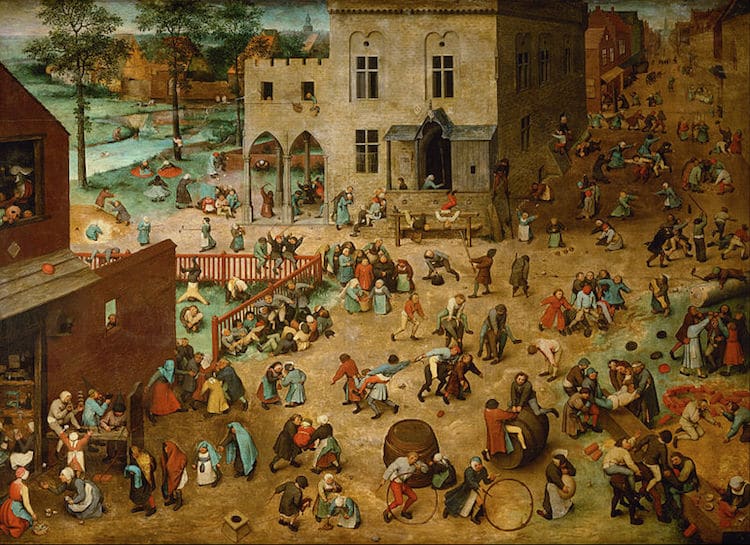

Image Courtesy of My Modern Met
Naturalism
It is an artistic approach that began in the early stages of the and it aims to depict the world and individuals in great detail and precision. Here are a few important artists that implemented :
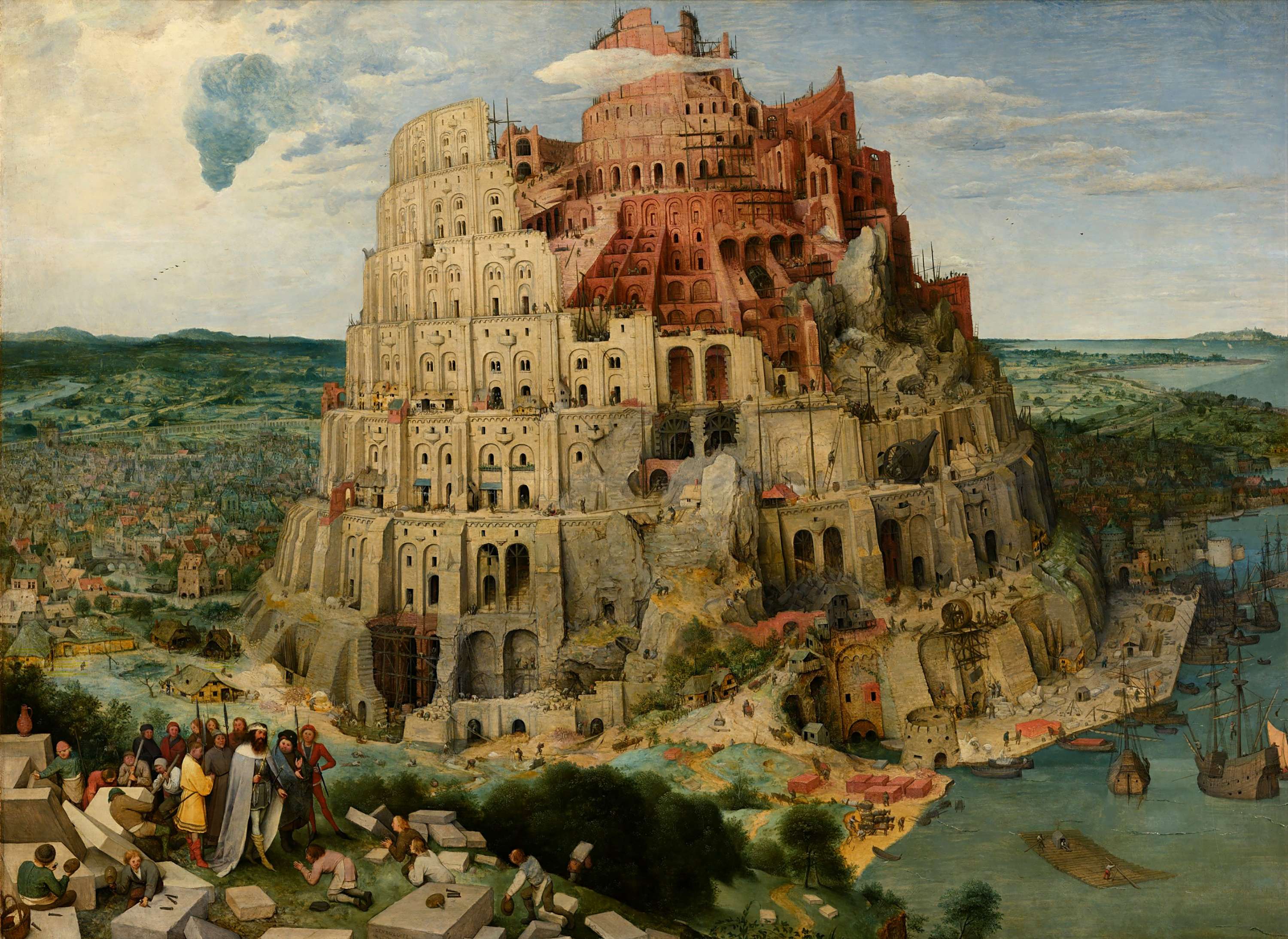

Note in the piece above the amount of detail and the symbolism of the idea of "rebirth."
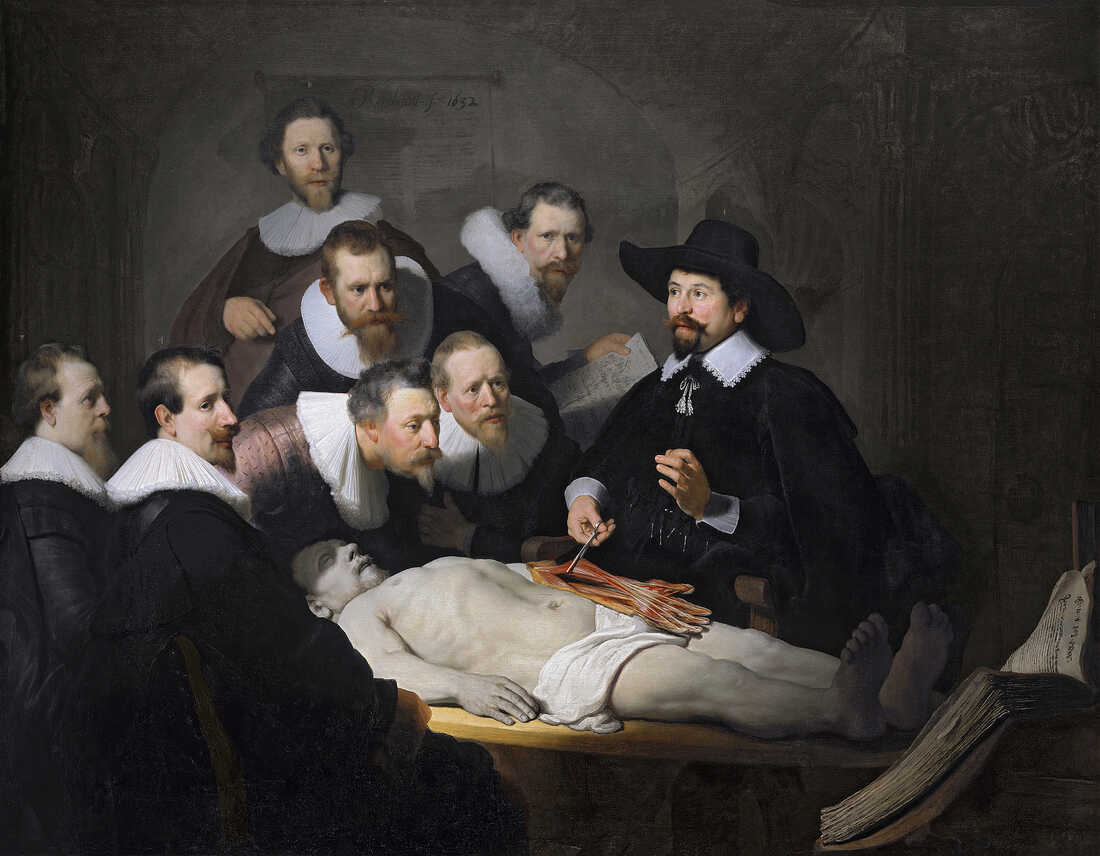
Note the subjects of the picture above and the precision of their expression. The study of human anatomy became important during the Renaissance, and this piece represents the emergence of this area of interest.
After reading this guide, it is important that you are able to analyze the differences and simillarities in the development of Renaissance across different European regions.
🎥 Watch: AP European History
Key Terms to Review (19)
Belgium
: A small country located in Western Europe known for its medieval towns and Renaissance architecture. It played a key role in both World Wars.Catholic teachings
: Catholic teachings refer to the doctrines, beliefs, and practices upheld by the Roman Catholic Church. These include concepts like the Holy Trinity, sacraments, papal infallibility, and others.Christian Humanism
: A Renaissance movement that combined Christian faith with classical humanist principles, emphasizing intellectual freedom, individualism, and the study of humanities to improve society.Classical Text
: A classical text is a work of literature that has stood the test of time and is widely recognized for its literary merit, historical significance, or cultural impact. These texts often originate from ancient Greece or Rome.England
: A country that is part of the United Kingdom. It was a major player in the Industrial Revolution and colonialism, shaping much of modern Western history.Erasmus
: Erasmus was a Dutch Renaissance humanist, Catholic priest, social critic, teacher, and theologian. He is best known for his critical editions of the New Testament and his advocacy for religious tolerance.France
: France is a country located in Western Europe. Known for its cultural influence, it has played a central role in European history from the French Revolution to both World Wars.Germany
: Germany is a country located in Central Europe. It played a significant role in many historical events such as World War I & II, Reformation, Cold War etc., shaping much of European history.Johann Gutenberg
: A German blacksmith, goldsmith, printer, and publisher who introduced printing to Europe with the invention of mechanical movable type printing.Latin text of the Church
: The Latin text refers to scriptures, liturgy, and theological writings used in Western Christianity (primarily Roman Catholicism) that are written in Latin - often referred to as Ecclesiastical Latin or Church Latin.Naturalism
: Naturalism is an artistic movement characterized by detailed, realistic portrayals of nature or human life with an emphasis on the deterministic aspects of existence (the belief that all events are predetermined).Netherlands
: A Northwestern European nation known for its flat landscape characterized by canals, tulip fields, windmills and cycling routes. It's also famous for being one of the world's top exporters of goods.New Testament
: The second part of Christian Bible, consisting mainly of narratives about Jesus Christ's life teachings, death, resurrection along with writings by early Christian leaders.Northern Renaissance
: The Northern Renaissance refers to the period of Renaissance that occurred in Europe north of the Alps. Unlike the Italian Renaissance that was influenced by Ancient Rome, this period was characterized by a greater emphasis on religion and less focus on the classical antiquity.Pieter Bruegel the Elder
: Pieter Bruegel the Elder was a Netherlandish artist from the 16th century known for his landscapes and peasant scenes which were innovative depictions at this time period.Printing Press
: A machine invented by Johann Gutenberg that creates copies of texts through an impression on a paper sheet—an innovation that revolutionized book production and distribution during Renaissance Europe.Protestant Reformation
: The Protestant Reformation was a major 16th century European movement aimed initially at reforming the beliefs and practices of the Roman Catholic Church. Its religious aspects were supplemented by ambitious political rulers who wanted to extend their power and control at the expense of the Church.Rembrandt
: Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (1606-1669) was a Dutch painter and etcher. He is generally considered one of the greatest painters and printmakers in European art history and the most important in Dutch history.Secularism
: The principle of separation of the state from religious institutions. It asserts the freedom of religion, and freedom from religion, within a state that is neutral on matters of belief.1.3 Northern Renaissance
3 min read•january 7, 2023
Christine Lin
Isabela Padilha Vilela
Christine Lin
Isabela Padilha Vilela
The Northern Renaissance
The occurred after the Italian Renaissance, in the beginning of the 15th century. It affected northern countries in Europe such as , , , and the .
The and its scholars were a catalyst for the , in part because they began reading the original ⛪ and recognized discrepancies between those readings and the . Those in the were from diverse backgrounds and were passionate about religious reform, unlike those in the Italian Renaissance.
The biggest societal change during the was the invention of the by . The 🖶 with moveable type was created in during the 15th century. This invention led to the ability for the Church, northern humanists, and statesmen to spread their ideas and viewpoints to a wider audience and books on religion as well.
The is characterized by the idea of Christian Humanism 🧍♀️in which the teachings of Christianity were shaped to incorporate the meaning of the individual (what is it to be human?) in their studies. The "prince of humanism" was , a Dutch humanist and scholar that wrote several criticisms to the imposition of power and corruption of the Catholic Church. But, he was still a devout Christian and committed to the church. His version of the "" shaped modern biblical scholarship.
🎥 Watch: AP Euro - Northern Renaissance
The impact of the Northern Renaissance
The , with the new values in and individualism that challenge religious, political and intellectual institutions, focused heavily on religious reforms. As arose, religious reform and the creation of new religious sectors away from the Catholic Church was promoted.
The most important part of the is the printing press. As mentioned before, it led to an increase in literacy, which led to individuals beginning to question religious text and in turn, led to the demand for religious reform across northern Europe.
Italian Renaissance vs. Northern Renaissance
Italian Renaissance:
Heavily emphasized on the teaching of 📖
Less detailed depictions in art of everyday life “” and more mythological deceptions
Linked less on Religious issues, but more in intellectual reforms in history, literature and human anatomy

Image Courtesy of Artyfactory
Northern Renaissance:
Studied less on Classical texts
More domestic and religious depictions in art🎨 and everyday life (in greater detail)
Linked more with religious issues and reforms (the religious reforms that challenged and questioned❔ the practices of the Church)

Image Courtesy of My Modern Met
Naturalism
It is an artistic approach that began in the early stages of the and it aims to depict the world and individuals in great detail and precision. Here are a few important artists that implemented :

Note in the piece above the amount of detail and the symbolism of the idea of "rebirth."

Note the subjects of the picture above and the precision of their expression. The study of human anatomy became important during the Renaissance, and this piece represents the emergence of this area of interest.
After reading this guide, it is important that you are able to analyze the differences and simillarities in the development of Renaissance across different European regions.
🎥 Watch: AP European History
Key Terms to Review (19)
Belgium
: A small country located in Western Europe known for its medieval towns and Renaissance architecture. It played a key role in both World Wars.Catholic teachings
: Catholic teachings refer to the doctrines, beliefs, and practices upheld by the Roman Catholic Church. These include concepts like the Holy Trinity, sacraments, papal infallibility, and others.Christian Humanism
: A Renaissance movement that combined Christian faith with classical humanist principles, emphasizing intellectual freedom, individualism, and the study of humanities to improve society.Classical Text
: A classical text is a work of literature that has stood the test of time and is widely recognized for its literary merit, historical significance, or cultural impact. These texts often originate from ancient Greece or Rome.England
: A country that is part of the United Kingdom. It was a major player in the Industrial Revolution and colonialism, shaping much of modern Western history.Erasmus
: Erasmus was a Dutch Renaissance humanist, Catholic priest, social critic, teacher, and theologian. He is best known for his critical editions of the New Testament and his advocacy for religious tolerance.France
: France is a country located in Western Europe. Known for its cultural influence, it has played a central role in European history from the French Revolution to both World Wars.Germany
: Germany is a country located in Central Europe. It played a significant role in many historical events such as World War I & II, Reformation, Cold War etc., shaping much of European history.Johann Gutenberg
: A German blacksmith, goldsmith, printer, and publisher who introduced printing to Europe with the invention of mechanical movable type printing.Latin text of the Church
: The Latin text refers to scriptures, liturgy, and theological writings used in Western Christianity (primarily Roman Catholicism) that are written in Latin - often referred to as Ecclesiastical Latin or Church Latin.Naturalism
: Naturalism is an artistic movement characterized by detailed, realistic portrayals of nature or human life with an emphasis on the deterministic aspects of existence (the belief that all events are predetermined).Netherlands
: A Northwestern European nation known for its flat landscape characterized by canals, tulip fields, windmills and cycling routes. It's also famous for being one of the world's top exporters of goods.New Testament
: The second part of Christian Bible, consisting mainly of narratives about Jesus Christ's life teachings, death, resurrection along with writings by early Christian leaders.Northern Renaissance
: The Northern Renaissance refers to the period of Renaissance that occurred in Europe north of the Alps. Unlike the Italian Renaissance that was influenced by Ancient Rome, this period was characterized by a greater emphasis on religion and less focus on the classical antiquity.Pieter Bruegel the Elder
: Pieter Bruegel the Elder was a Netherlandish artist from the 16th century known for his landscapes and peasant scenes which were innovative depictions at this time period.Printing Press
: A machine invented by Johann Gutenberg that creates copies of texts through an impression on a paper sheet—an innovation that revolutionized book production and distribution during Renaissance Europe.Protestant Reformation
: The Protestant Reformation was a major 16th century European movement aimed initially at reforming the beliefs and practices of the Roman Catholic Church. Its religious aspects were supplemented by ambitious political rulers who wanted to extend their power and control at the expense of the Church.Rembrandt
: Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (1606-1669) was a Dutch painter and etcher. He is generally considered one of the greatest painters and printmakers in European art history and the most important in Dutch history.Secularism
: The principle of separation of the state from religious institutions. It asserts the freedom of religion, and freedom from religion, within a state that is neutral on matters of belief.
Resources
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.