
1.7 Colonial Rivals
3 min read•january 8, 2023
Christine Lin
Isabela Padilha Vilela
Christine Lin
Isabela Padilha Vilela
Effects of European Expansion
Spain & Portugal
With Spain and Portugal beginning to establish colonies overseas, many other European countries became determined to do the same, causing rivalry between the countries🌊. The Spanish established colonies in the Americas, the Caribbean and the Pacific which made Spain the dominant state in Europe in the 1500s. Portugal also owned a significant part of the territory in the Americas, and later acquired lands in Africa, Asia and Ocenia as well. France, England and the Netherlands later established colonies and trading networks that competed with Portuguese and Spanish dominance in the 1600s.
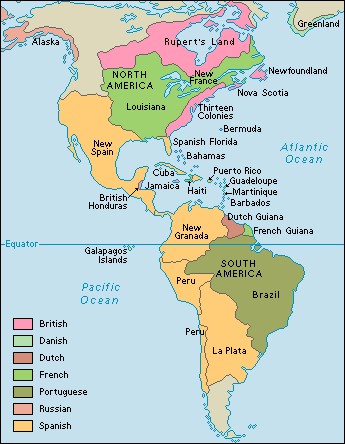
Dutch
The Dutch began exploring in the early 1600s and colonized New York, thanks to and his exploration efforts. Their power led to the creation of the in South Africa, resulting in the Dutch taking over many of Portugal’s trading posts.
The Dutch were able to gain power due to political, economic, religious, and societal means. The Dutch had autonomous provinces which were governed by , the largest merchant marines in Europe, spread , and their religious and intellectual tolerance allowed for economic growth to prosper.

Image Courtesy of Legends of America
France
The French had three motives behind their explorations: fish, fur, and faith. The established profitable with the use of . They also went to India but were unable to defeat the British and were forced to leave after the Seven Years War.
The Conflicts
Here are some of the most popular/important conflicts that happened between these European nations over colonization:
Asiento - Contract signed by the Spanish crown with a private company that allowed the selling of in their colonies. Although the contract was initially made for Portugal, this right was later expanded to many other European nations. The enslaved several Africans and increased economic competition between these nations.
- This conflict began with the death of , who had no heirs, causing a succession crisis. Other European nations feared the control of France over Spain, since Charles had bequeathed the grandon of the throne. Other European nations that opposed Philip's taking of the throne engaged in the fight. It was ended through the and recognized Philip and the King of Spain.
- This conflict was fought between most major countries in Europe, and it was sparked by conflicts faced on the domination of Europe and tensions in colonial territories. It was ended by the .
- Treaty that settled land conflicts in South America between Portugal and Spain. The treat laid out a line on the map that separated the land that was owned by Portugal (the east) and by Spain (west of the treaty line).
🎥 Watch: AP European History - Age of Exploration
Key Terms to Review (19)
African Slaves
: African slaves were individuals from Africa who were captured and sold into slavery, primarily to European colonies in the Americas during the 15th to 19th centuries. This was part of the Atlantic Slave Trade.Asiento System
: A Spanish practice of granting a foreign power or individual a monopoly on the slave trade within certain colonies. This was used as a means of controlling commerce in their empire.Calvinism
: Calvinism is a major branch of Protestant Christianity that follows the theological traditions and teachings of John Calvin, emphasizing predestination and absolute sovereignty of God.Dutch East India Company
: The Dutch East India Company was a powerful company established by royal charter in 1602 to establish and direct trade throughout Asia.Effects of European Expansion
: The effects of European expansion refer to the changes and impacts that occurred as a result of Europe's exploration, colonization, and trade with other parts of the world from the 15th century onwards.French Colony of Haiti
: The French Colony of Haiti (Saint-Domingue) was a French colony on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola from 1659 to 1804, known for its wealth derived from plantation agriculture and African slave labor.Henry Hudson
: Henry Hudson was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of northeastern United States.King Charles II of Spain
: King Charles II was the last Habsburg ruler from 1665 until his death in 1700. He had no direct heirs, leading to a succession crisis upon his death known as The War Of The Spanish Succession.King Louis XIV of France
: Known as 'The Sun King', Louis XIV ruled France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign is associated with absolute monarchy, territorial expansionism and centralization of power.Merchant Oligarchies
: A merchant oligarchy is a form of government where political power is in the hands of a small group of wealthy merchants or business leaders.Portuguese Colonies
: These were territories around the world that were discovered, conquered, and ruled by Portugal from the 15th to 20th centuries. They played a crucial role in the Age of Discovery and established Portugal as a global power.Seven Years' War
: The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict involving many European powers but primarily fought between France and Britain. It resulted in significant territorial changes and set stage for future conflicts.Spain & Portugal
: Spain and Portugal are two neighboring countries located on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. They were leading nations during the Age of Discovery in 15th-17th centuries.Spanish Colonies
: Spanish colonies refer to territories that were controlled by Spain outside of Europe from the late 15th century until the early 19th century, primarily in the Americas and Asia.Sugar Plantations
: Large-scale farms in the New World, particularly in the Caribbean and Brazil during the 16th to 19th centuries, where sugar cane was grown and processed primarily for export.Treaty of Paris
: The Treaty of Paris, signed in 1783, ended the American Revolutionary War and recognized the United States as an independent nation.Treaty of Tordesillas
: The Treaty of Tordesillas, signed in 1494, was an agreement between Spain and Portugal aimed at settling conflicts over lands newly discovered or explored by Christopher Columbus and other late 15th-century voyagers.Treaty of Utrecht
: The Treaty of Utrecht, signed in 1713, ended the War of Spanish Succession. It marked the rise of British power and significantly reduced French influence in Europe.War of the Spanish Succession
: The War of the Spanish Succession (1701-1714) was a major European conflict triggered by the death of the childless King Charles II of Spain. It involved several European powers who were trying to prevent the union of French and Spanish thrones under one monarch, which could disrupt the balance of power in Europe.1.7 Colonial Rivals
3 min read•january 8, 2023
Christine Lin
Isabela Padilha Vilela
Christine Lin
Isabela Padilha Vilela
Effects of European Expansion
Spain & Portugal
With Spain and Portugal beginning to establish colonies overseas, many other European countries became determined to do the same, causing rivalry between the countries🌊. The Spanish established colonies in the Americas, the Caribbean and the Pacific which made Spain the dominant state in Europe in the 1500s. Portugal also owned a significant part of the territory in the Americas, and later acquired lands in Africa, Asia and Ocenia as well. France, England and the Netherlands later established colonies and trading networks that competed with Portuguese and Spanish dominance in the 1600s.

Dutch
The Dutch began exploring in the early 1600s and colonized New York, thanks to and his exploration efforts. Their power led to the creation of the in South Africa, resulting in the Dutch taking over many of Portugal’s trading posts.
The Dutch were able to gain power due to political, economic, religious, and societal means. The Dutch had autonomous provinces which were governed by , the largest merchant marines in Europe, spread , and their religious and intellectual tolerance allowed for economic growth to prosper.

Image Courtesy of Legends of America
France
The French had three motives behind their explorations: fish, fur, and faith. The established profitable with the use of . They also went to India but were unable to defeat the British and were forced to leave after the Seven Years War.
The Conflicts
Here are some of the most popular/important conflicts that happened between these European nations over colonization:
Asiento - Contract signed by the Spanish crown with a private company that allowed the selling of in their colonies. Although the contract was initially made for Portugal, this right was later expanded to many other European nations. The enslaved several Africans and increased economic competition between these nations.
- This conflict began with the death of , who had no heirs, causing a succession crisis. Other European nations feared the control of France over Spain, since Charles had bequeathed the grandon of the throne. Other European nations that opposed Philip's taking of the throne engaged in the fight. It was ended through the and recognized Philip and the King of Spain.
- This conflict was fought between most major countries in Europe, and it was sparked by conflicts faced on the domination of Europe and tensions in colonial territories. It was ended by the .
- Treaty that settled land conflicts in South America between Portugal and Spain. The treat laid out a line on the map that separated the land that was owned by Portugal (the east) and by Spain (west of the treaty line).
🎥 Watch: AP European History - Age of Exploration
Key Terms to Review (19)
African Slaves
: African slaves were individuals from Africa who were captured and sold into slavery, primarily to European colonies in the Americas during the 15th to 19th centuries. This was part of the Atlantic Slave Trade.Asiento System
: A Spanish practice of granting a foreign power or individual a monopoly on the slave trade within certain colonies. This was used as a means of controlling commerce in their empire.Calvinism
: Calvinism is a major branch of Protestant Christianity that follows the theological traditions and teachings of John Calvin, emphasizing predestination and absolute sovereignty of God.Dutch East India Company
: The Dutch East India Company was a powerful company established by royal charter in 1602 to establish and direct trade throughout Asia.Effects of European Expansion
: The effects of European expansion refer to the changes and impacts that occurred as a result of Europe's exploration, colonization, and trade with other parts of the world from the 15th century onwards.French Colony of Haiti
: The French Colony of Haiti (Saint-Domingue) was a French colony on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola from 1659 to 1804, known for its wealth derived from plantation agriculture and African slave labor.Henry Hudson
: Henry Hudson was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of northeastern United States.King Charles II of Spain
: King Charles II was the last Habsburg ruler from 1665 until his death in 1700. He had no direct heirs, leading to a succession crisis upon his death known as The War Of The Spanish Succession.King Louis XIV of France
: Known as 'The Sun King', Louis XIV ruled France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign is associated with absolute monarchy, territorial expansionism and centralization of power.Merchant Oligarchies
: A merchant oligarchy is a form of government where political power is in the hands of a small group of wealthy merchants or business leaders.Portuguese Colonies
: These were territories around the world that were discovered, conquered, and ruled by Portugal from the 15th to 20th centuries. They played a crucial role in the Age of Discovery and established Portugal as a global power.Seven Years' War
: The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict involving many European powers but primarily fought between France and Britain. It resulted in significant territorial changes and set stage for future conflicts.Spain & Portugal
: Spain and Portugal are two neighboring countries located on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. They were leading nations during the Age of Discovery in 15th-17th centuries.Spanish Colonies
: Spanish colonies refer to territories that were controlled by Spain outside of Europe from the late 15th century until the early 19th century, primarily in the Americas and Asia.Sugar Plantations
: Large-scale farms in the New World, particularly in the Caribbean and Brazil during the 16th to 19th centuries, where sugar cane was grown and processed primarily for export.Treaty of Paris
: The Treaty of Paris, signed in 1783, ended the American Revolutionary War and recognized the United States as an independent nation.Treaty of Tordesillas
: The Treaty of Tordesillas, signed in 1494, was an agreement between Spain and Portugal aimed at settling conflicts over lands newly discovered or explored by Christopher Columbus and other late 15th-century voyagers.Treaty of Utrecht
: The Treaty of Utrecht, signed in 1713, ended the War of Spanish Succession. It marked the rise of British power and significantly reduced French influence in Europe.War of the Spanish Succession
: The War of the Spanish Succession (1701-1714) was a major European conflict triggered by the death of the childless King Charles II of Spain. It involved several European powers who were trying to prevent the union of French and Spanish thrones under one monarch, which could disrupt the balance of power in Europe.
Resources
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.