
8.4 Effect of Density of Populations
3 min read•january 13, 2023
Caroline Koffke
Jed Quiaoit
Caroline Koffke
Jed Quiaoit
A population can produce a density of individuals that exceeds the system’s resource availability. When this occurs, the population experiences competition for resources, and the growth rate of the population begins to decline. This is known as overpopulation. 😲
Overpopulation can occur when the population exceeds the carrying capacity of the ecosystem, which is the maximum number of individuals that can be supported by the available resources. Overpopulation can lead to depletion of resources, increased competition for resources, and a decline in the overall health and fitness of the population.
Density-Dependent Factors vs. Density-Independent Factors
As a refresher: populations are often affected by factors that inhibit their ability to continue to survive and reproduce. These factors may be broken into two categories: density-dependent factors and density-independent factors.
In genera, density-dependent factors are factors that affect the growth rate of a population in relation to its density. For example, competition for resources and predation are density-dependent factors. Density-independent factors are factors that affect the growth rate of a population regardless of its density. For example, natural disasters, such as floods or droughts, are density-independent factors. 🌊
Density-Dependent Factors
Density-dependent factors are factors in the environment that affects populations differently depending on the size of the population. As the population size increases, the effects of the density-dependent factors increase as well. Examples of density-dependent factors are access to food, the amount of predators, disease, and migration.
All of these factors depend on the number of organisms in the population. A small population is less susceptible to a decrease in food than a large population that requires a lot of resources. The density-dependent factor that has the most impact on populations is access to food.
Density-Independent Factors
Density-independent factors are factors in the environment that can affect a population regardless of size. Examples of density-independent factors are weather and climate.
Right now, the warming of the planet is greatly affecting populations, regardless of their size. This warming can lead to a loss of habitat, an inability to adapt to temperatures, and a loss of water or food sources. All of these factors can be devastating to a population.
Carrying Capacity
As limits to growth due to density-dependent and density-independent factors are imposed, a logistic growth model generally ensues. 🧳
The logistic growth model is a mathematical model that describes how a population's growth rate changes over time in response to these limits to growth. The logistic model predicts that the growth rate of a population will start off high and then decline as the population approaches the carrying capacity of the ecosystem. Once the carrying capacity is reached, the population's growth rate will stabilize and eventually decline, resulting in an equilibrium population size.
Both density-dependent and density-independent factors lead to a limit in the number of organisms that can survive in an environment. This limit is known as the carrying capacity.
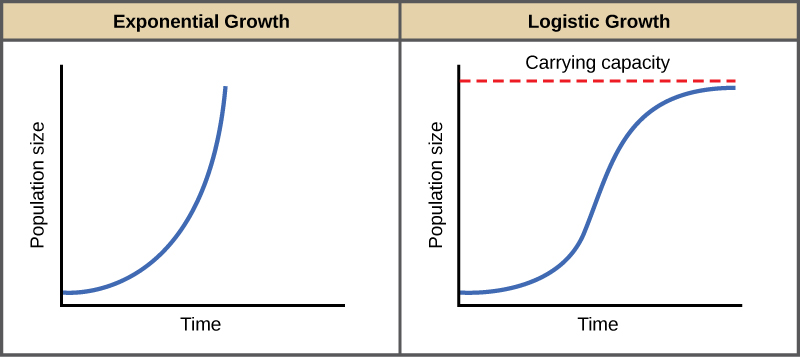
Image courtesy of WikiMedia Commons.
When carrying capacity is in place, logarithmic growth is no longer possible. Instead, ecologists measure logistic growth. This can be calculated with the following equation:

Example: In a population of 862 iguanas, the per capita growth rate is 0.05, and the carrying capacity is 1000. What is the change in population after one year? 🦎

The population of iguanas increased by 6 in one year!
Key Terms to Review (13)
Access to Food
: Access to food refers to one's ability to acquire safe and nutritious food consistently for maintaining an active and healthy life. It involves affordability, allocation resources and preference.Carrying Capacity
: The maximum number of individuals of a particular species that an environment can support indefinitely under stable conditions.Competition for Resources
: This is a biological concept where organisms vie for the same limited resources in an environment, such as food, water, light, space or mates.Density-Dependent Factors
: Density-dependent factors are elements that affect the population growth rate depending on how dense the population is. These can include competition, predation, disease and food availability.Density-Independent Factors
: These are environmental factors that affect a population's size regardless of its density. They include natural disasters, climate, and human activities.Disease
: A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not due to any immediate external injury.Equilibrium Population Size
: The equilibrium population size is the number of individuals in a species that an environment can sustain indefinitely without any significant changes in availability of resources.Logistic Growth Model
: Logistic growth model describes how population growth may start slowly, then increase rapidly until reaching carrying capacity due to environmental resistance such as limited resources.Migration
: In biology terms, migration refers to the movement and exchange of genes from one population to another, which can affect the genetic diversity of the populations.Natural Disasters
: Natural disasters are extreme, sudden events caused by environmental factors that injure people and damage property. They include earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, tornadoes, wildfires, tsunamis, and other geologic processes.Overpopulation
: Overpopulation refers to a situation where the number of organisms in a particular habitat exceeds the carrying capacity, leading to resource depletion and environmental degradation.Predation
: Predation is an interaction where one organism (the predator) kills another (the prey) for food.Weather and Climate
: Weather refers to short-term atmospheric conditions while climate is the weather pattern over a long period (30 years or more).8.4 Effect of Density of Populations
3 min read•january 13, 2023
Caroline Koffke
Jed Quiaoit
Caroline Koffke
Jed Quiaoit
A population can produce a density of individuals that exceeds the system’s resource availability. When this occurs, the population experiences competition for resources, and the growth rate of the population begins to decline. This is known as overpopulation. 😲
Overpopulation can occur when the population exceeds the carrying capacity of the ecosystem, which is the maximum number of individuals that can be supported by the available resources. Overpopulation can lead to depletion of resources, increased competition for resources, and a decline in the overall health and fitness of the population.
Density-Dependent Factors vs. Density-Independent Factors
As a refresher: populations are often affected by factors that inhibit their ability to continue to survive and reproduce. These factors may be broken into two categories: density-dependent factors and density-independent factors.
In genera, density-dependent factors are factors that affect the growth rate of a population in relation to its density. For example, competition for resources and predation are density-dependent factors. Density-independent factors are factors that affect the growth rate of a population regardless of its density. For example, natural disasters, such as floods or droughts, are density-independent factors. 🌊
Density-Dependent Factors
Density-dependent factors are factors in the environment that affects populations differently depending on the size of the population. As the population size increases, the effects of the density-dependent factors increase as well. Examples of density-dependent factors are access to food, the amount of predators, disease, and migration.
All of these factors depend on the number of organisms in the population. A small population is less susceptible to a decrease in food than a large population that requires a lot of resources. The density-dependent factor that has the most impact on populations is access to food.
Density-Independent Factors
Density-independent factors are factors in the environment that can affect a population regardless of size. Examples of density-independent factors are weather and climate.
Right now, the warming of the planet is greatly affecting populations, regardless of their size. This warming can lead to a loss of habitat, an inability to adapt to temperatures, and a loss of water or food sources. All of these factors can be devastating to a population.
Carrying Capacity
As limits to growth due to density-dependent and density-independent factors are imposed, a logistic growth model generally ensues. 🧳
The logistic growth model is a mathematical model that describes how a population's growth rate changes over time in response to these limits to growth. The logistic model predicts that the growth rate of a population will start off high and then decline as the population approaches the carrying capacity of the ecosystem. Once the carrying capacity is reached, the population's growth rate will stabilize and eventually decline, resulting in an equilibrium population size.
Both density-dependent and density-independent factors lead to a limit in the number of organisms that can survive in an environment. This limit is known as the carrying capacity.

Image courtesy of WikiMedia Commons.
When carrying capacity is in place, logarithmic growth is no longer possible. Instead, ecologists measure logistic growth. This can be calculated with the following equation:

Example: In a population of 862 iguanas, the per capita growth rate is 0.05, and the carrying capacity is 1000. What is the change in population after one year? 🦎

The population of iguanas increased by 6 in one year!
Key Terms to Review (13)
Access to Food
: Access to food refers to one's ability to acquire safe and nutritious food consistently for maintaining an active and healthy life. It involves affordability, allocation resources and preference.Carrying Capacity
: The maximum number of individuals of a particular species that an environment can support indefinitely under stable conditions.Competition for Resources
: This is a biological concept where organisms vie for the same limited resources in an environment, such as food, water, light, space or mates.Density-Dependent Factors
: Density-dependent factors are elements that affect the population growth rate depending on how dense the population is. These can include competition, predation, disease and food availability.Density-Independent Factors
: These are environmental factors that affect a population's size regardless of its density. They include natural disasters, climate, and human activities.Disease
: A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not due to any immediate external injury.Equilibrium Population Size
: The equilibrium population size is the number of individuals in a species that an environment can sustain indefinitely without any significant changes in availability of resources.Logistic Growth Model
: Logistic growth model describes how population growth may start slowly, then increase rapidly until reaching carrying capacity due to environmental resistance such as limited resources.Migration
: In biology terms, migration refers to the movement and exchange of genes from one population to another, which can affect the genetic diversity of the populations.Natural Disasters
: Natural disasters are extreme, sudden events caused by environmental factors that injure people and damage property. They include earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, tornadoes, wildfires, tsunamis, and other geologic processes.Overpopulation
: Overpopulation refers to a situation where the number of organisms in a particular habitat exceeds the carrying capacity, leading to resource depletion and environmental degradation.Predation
: Predation is an interaction where one organism (the predator) kills another (the prey) for food.Weather and Climate
: Weather refers to short-term atmospheric conditions while climate is the weather pattern over a long period (30 years or more).
Resources
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.