
4.5 Homeostasis & Feedback Loops
4 min read•december 17, 2022
Annika Tekumulla
Haseung Jun
Annika Tekumulla
Haseung Jun
Homeostasis & Feedback Loops
Based upon the environment around the organism, the timing, and coordination, there can be either a positive or negative feedback. Organisms use feedback to maintain homeostasis as well as respond to the environment. Homeostasis is an important topic that College Board likes to focus on, so it's important to be able to explain any positive or off the top of your head. In this guide, we'll be looking at an example of each.
Negative Feedback Loops
are the response of reactions and leads to a decrease in those reactions. Negative loops also maintain homeostasis by creating optimal internal environments. Negative loops are also able to return a system back to target homeostasis.
An example of is . When you eat food, blood glucose level rises from the sugar you just ate. The has a sensor attached to it in the blood stream, so when glucose level rises, it senses the increase. It in turn releases into the blood. travels through the bloodstream and signals the that there is too much glucose in the blood stream. The then takes the glucose and stores it as (long chain of sugar). Then, blood glucose level declines, brining it back to the regular sugar level allowed by the body.
But what if your body is low on glucose level? This could cause problems too, so the body will respond to this stimulus. This time, the will sense the change again and release into the blood. will travel through the blood stream and signal the that the blood sugar level is low. The will break down the stored back into glucose and release it into the blood stream. As a result, blood glucose level rises, brining the body back to the regular sugar level.
Image courtesy of Lumen Learning.
would disrupt the negative feedback loop of . is a condition that can be caused by an imbalance of . There can be either too little or a resistance to . With , the body does not produce enough . This can simply be fixed by taking extra after meals. This way, even if the doesn't create enough , there will be enough to signal the .
is a little more problematic. In , the is essentially doesn't recognize . So even if you ate a ton of , your wouldn't recognize it and in turn wouldn't take glucose and store it as . This is why are harder to manage, because there isn't a clear solution to the problem. When there is a problem in the negative feedback loop, it can lead to high blood glucose levels that can lead to adverse health effects.
Positive Feedback Loops
are used to increase the change in the cell by amplifying or speeding up the process. can also be called “snowballing” effects. It is also important to remember that without a stop or counterbalance, the positive feedback loop can not be controlled.
An example of a positive feedback loop is . During labor, a chemical called is released. Labor is a positive feedback loop because causes a response for to intensify and occur quicker. is released into the bloodstream and it stimulates . When the head of the baby pushes against the cervix, the brain receives signals, which stimulates the to secrete . More leads to more frequent , and the loop keeps going. After the birth, the loop is interrupted, stretching and end, and the loop is finished.
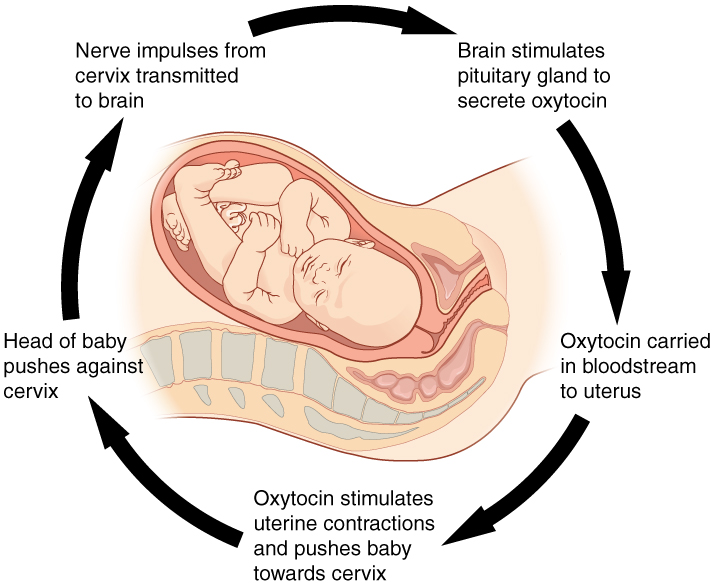
Image courtesy of BCcampus.
Ending Notes
Negative and are extremely important because it regulates the body. Homeostasis is the body's way of trying to keep it from changing to any extremes, so come into play with homeostasis. are important when more of this needs to create more of that.
Key Terms to Review (15)
Blood Sugar Regulation
: Blood sugar regulation involves maintaining glucose levels within narrow limits in the bloodstream for proper functioning of all cells in the body.Childbirth
: Childbirth refers to delivering a baby from its mother's uterus by means of contractions after gestation period ends at around 40 weeks.Contractions
: In biology context, contractions refer to rhythmic tightening and relaxing of uterine muscles during childbirth which help push baby out through birth canal.Diabetes
: Diabetes is a chronic disease where there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood due to either insufficient production or ineffective use of insulin.Glucagon
: Glucagon is a hormone produced by the pancreas that raises blood sugar levels by stimulating the breakdown of glycogen into glucose.Glycogen
: Glycogen is a polysaccharide that serves as the primary form of energy storage in animals and fungi. It's similar to starch but has more extensive branching.Insulin
: Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates the amount of glucose in the blood. It allows cells to take in glucose from the bloodstream and use it as energy.Liver
: The liver is a large organ that performs many essential functions related to digestion, metabolism, immunity, and storage of nutrients within the body.Negative Feedback Loops
: A negative feedback loop is a process in which the body senses a change and activates mechanisms to reverse that change.Oxytocin
: Oxytocin is a hormone produced in the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary gland. It plays a significant role in childbirth, breastfeeding, and social bonding.Pancreas
: The pancreas is an organ located behind stomach that produces enzymes used in digestion, as well as hormones like insulin and glucagon that regulate blood sugar levels.Pituitary Gland
: The pituitary gland is a small pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain. It is often referred to as the 'master gland' because it controls the function of most other endocrine glands.Positive Feedback Loops
: A positive feedback loop amplifies or increases changes; this tends to move a system away from its equilibrium state and make it more unstable.Type I Diabetes
: Type I Diabetes is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin, a hormone needed to allow sugar (glucose) to enter cells to produce energy.Type II Diabetes
: Type II Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body metabolizes sugar (glucose), with your body either resisting the effects of insulin or not producing enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels.4.5 Homeostasis & Feedback Loops
4 min read•december 17, 2022
Annika Tekumulla
Haseung Jun
Annika Tekumulla
Haseung Jun
Homeostasis & Feedback Loops
Based upon the environment around the organism, the timing, and coordination, there can be either a positive or negative feedback. Organisms use feedback to maintain homeostasis as well as respond to the environment. Homeostasis is an important topic that College Board likes to focus on, so it's important to be able to explain any positive or off the top of your head. In this guide, we'll be looking at an example of each.
Negative Feedback Loops
are the response of reactions and leads to a decrease in those reactions. Negative loops also maintain homeostasis by creating optimal internal environments. Negative loops are also able to return a system back to target homeostasis.
An example of is . When you eat food, blood glucose level rises from the sugar you just ate. The has a sensor attached to it in the blood stream, so when glucose level rises, it senses the increase. It in turn releases into the blood. travels through the bloodstream and signals the that there is too much glucose in the blood stream. The then takes the glucose and stores it as (long chain of sugar). Then, blood glucose level declines, brining it back to the regular sugar level allowed by the body.
But what if your body is low on glucose level? This could cause problems too, so the body will respond to this stimulus. This time, the will sense the change again and release into the blood. will travel through the blood stream and signal the that the blood sugar level is low. The will break down the stored back into glucose and release it into the blood stream. As a result, blood glucose level rises, brining the body back to the regular sugar level.
Image courtesy of Lumen Learning.
would disrupt the negative feedback loop of . is a condition that can be caused by an imbalance of . There can be either too little or a resistance to . With , the body does not produce enough . This can simply be fixed by taking extra after meals. This way, even if the doesn't create enough , there will be enough to signal the .
is a little more problematic. In , the is essentially doesn't recognize . So even if you ate a ton of , your wouldn't recognize it and in turn wouldn't take glucose and store it as . This is why are harder to manage, because there isn't a clear solution to the problem. When there is a problem in the negative feedback loop, it can lead to high blood glucose levels that can lead to adverse health effects.
Positive Feedback Loops
are used to increase the change in the cell by amplifying or speeding up the process. can also be called “snowballing” effects. It is also important to remember that without a stop or counterbalance, the positive feedback loop can not be controlled.
An example of a positive feedback loop is . During labor, a chemical called is released. Labor is a positive feedback loop because causes a response for to intensify and occur quicker. is released into the bloodstream and it stimulates . When the head of the baby pushes against the cervix, the brain receives signals, which stimulates the to secrete . More leads to more frequent , and the loop keeps going. After the birth, the loop is interrupted, stretching and end, and the loop is finished.

Image courtesy of BCcampus.
Ending Notes
Negative and are extremely important because it regulates the body. Homeostasis is the body's way of trying to keep it from changing to any extremes, so come into play with homeostasis. are important when more of this needs to create more of that.
Key Terms to Review (15)
Blood Sugar Regulation
: Blood sugar regulation involves maintaining glucose levels within narrow limits in the bloodstream for proper functioning of all cells in the body.Childbirth
: Childbirth refers to delivering a baby from its mother's uterus by means of contractions after gestation period ends at around 40 weeks.Contractions
: In biology context, contractions refer to rhythmic tightening and relaxing of uterine muscles during childbirth which help push baby out through birth canal.Diabetes
: Diabetes is a chronic disease where there are high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood due to either insufficient production or ineffective use of insulin.Glucagon
: Glucagon is a hormone produced by the pancreas that raises blood sugar levels by stimulating the breakdown of glycogen into glucose.Glycogen
: Glycogen is a polysaccharide that serves as the primary form of energy storage in animals and fungi. It's similar to starch but has more extensive branching.Insulin
: Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates the amount of glucose in the blood. It allows cells to take in glucose from the bloodstream and use it as energy.Liver
: The liver is a large organ that performs many essential functions related to digestion, metabolism, immunity, and storage of nutrients within the body.Negative Feedback Loops
: A negative feedback loop is a process in which the body senses a change and activates mechanisms to reverse that change.Oxytocin
: Oxytocin is a hormone produced in the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary gland. It plays a significant role in childbirth, breastfeeding, and social bonding.Pancreas
: The pancreas is an organ located behind stomach that produces enzymes used in digestion, as well as hormones like insulin and glucagon that regulate blood sugar levels.Pituitary Gland
: The pituitary gland is a small pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain. It is often referred to as the 'master gland' because it controls the function of most other endocrine glands.Positive Feedback Loops
: A positive feedback loop amplifies or increases changes; this tends to move a system away from its equilibrium state and make it more unstable.Type I Diabetes
: Type I Diabetes is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin, a hormone needed to allow sugar (glucose) to enter cells to produce energy.Type II Diabetes
: Type II Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body metabolizes sugar (glucose), with your body either resisting the effects of insulin or not producing enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels.
Resources
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.